This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Employers should think twice before implementing peer recognition programs
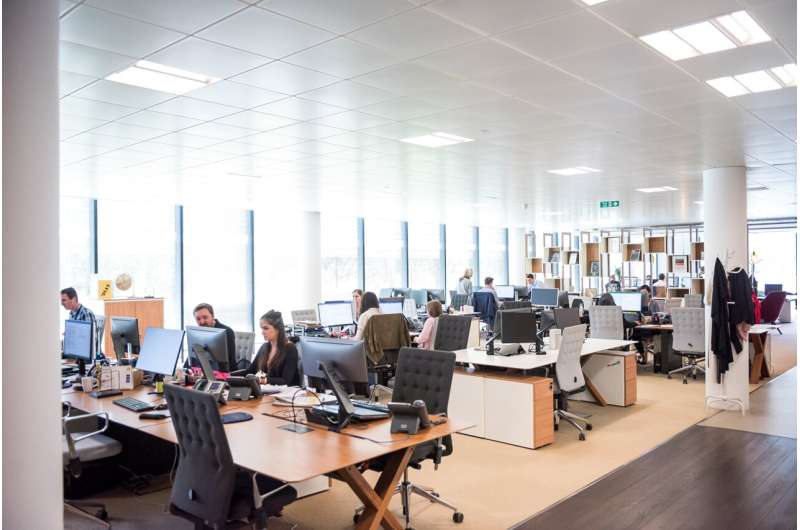

In fast-paced and often rapidly changing work environments, employers continue to seek new and improved ways to recognize employees in the workplace. However, new research from the University of Waterloo suggests that public peer recognition may backfire by enabling comparisons among employees, and these comparisons may make some employees feel unfairly treated.
"Employers have sought out various peer recognition systems in an effort to promote employee helping behavior," said Pei Wang, Ph.D. candidate in accounting at Waterloo. "When employees feel that they deserve recognition from their peers but do not receive it, employees can conclude that they are unfairly treated, and this makes employees less willing to help other co-workers, not only the co-worker they feel treated them unfairly,".
In practice, this type of treatment an employee interprets as unfair can occur when an individual disagrees regarding what type of behavior should and should not be recognized during public peer recognition. In addition, some employees may only provide recognition to those close to them.
Using a three-employee setting composed of the recognizer, the helper and the worker, the researcher tests whether peer information disclosed by peer recognition systems affects employees' subsequent willingness to help. During this study, both the helper and the worker assist the recognizer, however, only the helper receives recognition by the recognizer. The worker exhibits less willingness to assist the recognizer and the helper when the worker perceives that their initial assistance exceeds the helper's than when the worker perceives that their initial assistance is less than that of the helper's. The worker's lower level of willingness to assist the helper is a spillover from the reciprocal reaction to the recognizer's non-recognition.
These findings provide the first empirical evidence of the negative impact that peer recognition systems have on helping behavior. This research can inform how employers utilize peer recognition in the workplace. Peer recognition is often advertised as a tool to make employees more willing to help others. The study results show that managers may want to be mindful of the potential downside of enacting peer recognition.
"My research provides a first step in cautioning managers about a potential unintended consequence of using public peer recognition, and that is the perceived unfairness that reduces helping behavior," Wang said. It may be helpful for managers to communicate with their employees and come up with some agreed-upon guidelines on what should be recognized via public peer recognition and what does not need to be recognized via public peer recognition."
The study, "When peer recognition backfires: the impact of peer information on subsequent helping behavior," appears in the journal Accounting Perspectives.
More information: Pei Wang, When Peer Recognition Backfires: The Impact of Peer Information on Subsequent Helping Behavior†, Accounting Perspectives (2023). DOI: 10.1111/1911-3838.12335
Provided by University of Waterloo