This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
A slippery slope: Basic research underfunded in Australia, says study

A study co-led by The University of Queensland has found Australia is lagging behind similar countries in funding basic research, particularly in the medical, biotechnology and pharmaceutical sectors.
Dr. Lisette Pregelj from UQ's School of Chemistry and Molecular Biosciences analyzed funding and innovation data globally and found Australia's ability to develop innovative basic research was decreasing.
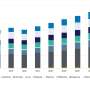
"Our ranking on the Global Innovation Index (GII) has been steadily waning over the past five years—25th place in 2022, down from 23rd in 2020, 22nd in 2019 and 20th in 2018," Dr. Pregelj said.
"But more concerning is the Index ranks us even lower for innovation outputs, with no sign of improvement over the past three years despite increased funding for commercialization.
"The World Intellectual Property Organization—which publishes publish the GII—also reports Australia produces fewer innovation outputs relative to its level of innovation investment.
"We're sliding down a slippery slope, and it needs to change."
The researchers found a lack of funding, particularly for basic research, may be contributing to the decline in innovation ranking. The research was published in March 2023 in Microbiology Australia.
"Figures from the OECD show Australia has reduced R&D investment as a percentage of GDP for the past 15 years, while other global economies have recorded an increase over the same period," Dr. Pregelj said.
"In 1996 almost 60% of Australia's higher education investment in research and development was in executing basic research, but by 2019 that figure had dropped to 40%.
"This has not been the case for the U.S. or China, which have each increased their proportions of higher education R&D investment in basic research.
"It's incredibly concerning to see Australia fall behind these international benchmarks."
Study co-lead Dr. Rosemary Harrison, a UQ alum and now biotechnology executive at TCR2 Therapeutics, said Australia needed to re-focus.
"Funding basic research for the sake of fundamental knowledge is crucial so Australia's innovation pipeline is well supported at its origins," Dr. Harrison said.
"We need to increase our total R&D investment to globally competitive levels, attract foreign investment and grow healthy local business, venture capital and private equity sectors responsible for funding primarily later-stage applied biopharmaceutical R&D.
"We welcome the announcement of the $15 billion National Reconstruction Fund but the balance of funding between basic and applied research will be critical.
"I know of so many excellent Australian basic researchers who have struggled to secure funding for nearly a decade—investing in them is an investment in our collective future."
More information: Rosemary S. Harrison et al, Restoring Australia's long-term innovation requires investment in basic research, Microbiology Australia (2023). DOI: 10.1071/MA23014
Provided by University of Queensland