This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
New fluorescent dyes help illuminate microscopic life
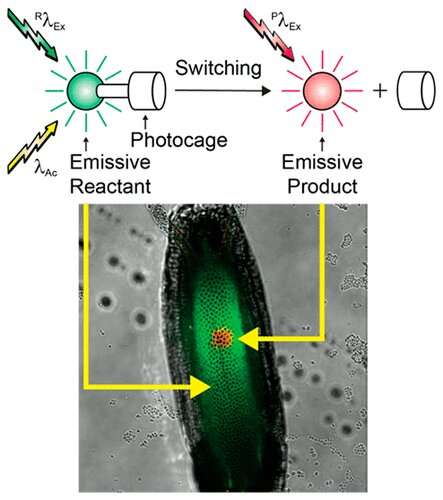
Inspired by the mechanism behind light-sensitive sunglasses, a team led by a North Carolina State University researcher invented a family of fluorescent dyes to illuminate biological processes at a very small scale—comparable in size to human hair.
The researchers described the mechanism behind the dyes in a publication in ACS Applied Optical Materials, led by Yang Zhang, assistant professor of textile engineering, chemistry and science at NC State.
The Abstract spoke to Zhang about how the dyes work.
The Abstract: How do these dyes work?
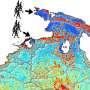
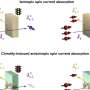
Yang Zhang: We designed a family of dyes called "photoactivatable fluorophores." These fluorescent dye molecules change color when they're hit by blue light irradiation. The dyes change color because part of the dye structure is photosensitive, and light irradiation changes their molecular structure. The dye conformations will emit light on a greener spectrum initially, and will emit red light after irradiation.
TA: How do the dyes fluoresce?
Zhang: It's like when human beings eat food, we absorb energy so we can do work, and then we go to bed to relax. After the molecule absorbs the energy, it wants to relax back to its ground state, so it relaxes and throws out the photons. The microscopic biological world is dark, and these dyes help to illuminate the biological processes with a microscope.
TA: How do you use them to illuminate microscopic processes?
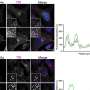
Zhang: We designed these dyes to be used with microscopy in basic biomedical research, although they have not been used in humans. We used the dyes to illuminate tiny transport molecules, or nanocarriers, diffusing within developing nematodes, or in developing flies. Those are typically hard to image using any other approaches.
Currently, we are exploring our dyes for single-molecule imaging, building upon work that won three scientists the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2014. This technique helps biomedical researchers investigate complicated life processes down to the nanoscale—in other words, at the molecular level.
TA: Do dyes like this exist already, and if so, how are the ones you worked on different?
Zhang: The dyes we worked on are brighter, and we think they are safer. That's because they emit light in the near-infrared region. You want to avoid having irradiation absorbed into tissue or cells. Also, we excite the cells by hitting them with light at a longer wavelength, so at a lower energy level. That will avoid heating up the cells, and potentially killing them. Our next steps are to look more closely at the phototoxicity levels to see how these dyes can be used more widely for single-molecule imaging.
More information: Yang Zhang et al, Photoactivatable Fluorophores for Bioimaging Applications, ACS Applied Optical Materials (2023). DOI: 10.1021/acsaom.3c00025
Provided by North Carolina State University