This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Researchers use TurboID to uncover new meiotic proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana

Meiotic recombination assures genetic variation during breeding. During meiotic prophase I, chromosomes are organized in a loop-base array by a proteinaceous structure called meiotic chromosome axis, which is critical for meiotic recombination and genetically diverse gametes. An international research team led by IPK Leibniz Institute reports the application of a TurboID-based approach to identify proteins in proximity of meiotic chromosome axes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Both known and new meiotic proteins were uncovered. The results have been published in the journal Nature Plants.
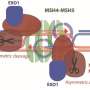
During meiosis, reshuffling of genetic information between homologous chromosomes through meiotic recombination creates variable gametes and hence genetic variation in offspring. Meiotic recombination occurs in the context of the meiotic chromosome axis, a proteinaceous structure along which sister chromatids are arranged in a loop-base array during prophase I. Data across organisms suggests meiotic chromosome axis serving as a scaffold for meiotic recombination.
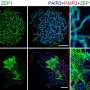
In the model plant A. thaliana, the axis associated proteins ASY1 and ASY3 are critical for synapsis and meiotic recombination. "Due to the key role of axis proteins such as ASY1 and ASY3 for meiotic fidelity including frequency and distribution of crossovers, further insights into the composition and regulation of plant meiotic chromosome axes are of interest," says Dr. Stefan Heckmann, head of IPK's independent research group Meiosis. However, plant proteomic studies aiming to dissect the composition and regulation of meiotic processes including the chromosome axes are hampered by a limited number of meiotic cells being embedded in floral organs.
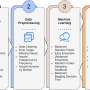
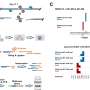
More recently proximity-dependent biotin identification (BioID) enabled the identification of proximate protein interactomes. BioID is based on the fusion of a protein of interest to a promiscuous biotin ligase that catalyzes biotinylation of proteins in proximity. "We apply an improved BioID version, termed TurboID, for proximity labeling of meiotic chromosome axis. We fused TurboID to axis-associated proteins ASY1 and ASY3 to identify their proximate interactomes in A. thaliana," says Dr. Stefan Heckmann. 39 ASY1 and/or ASY3 proximate candidates were identified. Besides known meiotic chromosome axis-related proteins, novel proteins that play a role during meiosis were also found.
"The successful application of TurboID in meiotic cells suggests that the employed method might be broadly applicable for rare cell types," says Dr. Chao Feng, first author of the study. "We envision that the data will foster future research on identified candidate proteins and that TurboID could be used for the identification of more yet unknown meiotic proteins or modifications."
More information: Stefan Heckmann, TurboID-based proteomic profiling of meiotic chromosome axes in Arabidopsis thaliana, Nature Plants (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41477-023-01371-7. www.nature.com/articles/s41477-023-01371-7
Journal information: Nature Plants
Provided by Leibniz Institute of Plant Genetics and Crop Plant Research