This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Purification of DNA nanostructures from hydrophobic aggregates
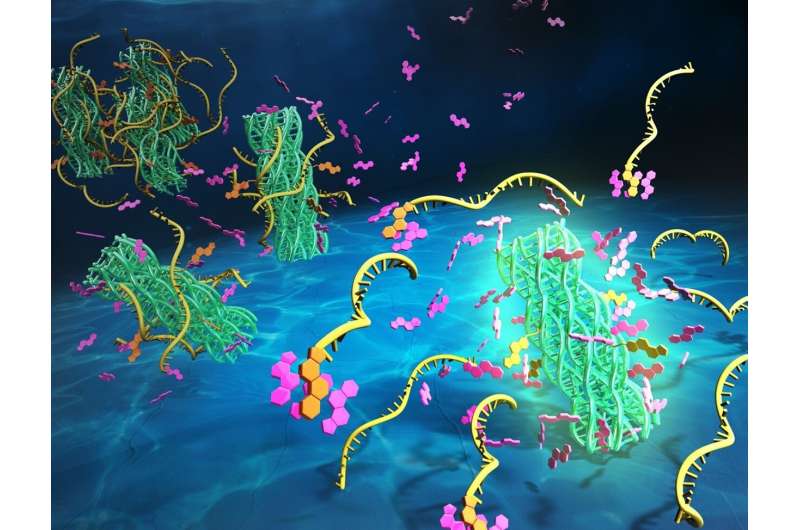
Researchers in Japan have developed a new method for purifying cholesterol-modified DNA nanostructures that could be used to functionalize molecular robot bodies (lipid vesicles). The study was a collaboration between Yusuke Sato of Kyushu Institute of Technology and Shin-ichiro M. Nomura of the Tohoku University, and the work was published in ChemBioChem.
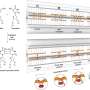
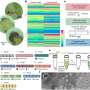
To purify the DNA nanostructures, the researchers first mixed surfactants with the materials for the DNA six-helix bundles with four cholesterol-modified DNA. Due to the hydrophobicity of the cholesterol, such DNA nanostructures were generally easy to aggregate in aqueous solution. The addition of surfactants helped to avoid the aggregation and allowed the purification of the target structures from the aggregates.
The researchers then separated the target DNA nanostructures from the aggregates by a gel electrophoresis. The separated DNA nanostructures were extracted from the gel.
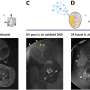
The scientists found that the surfactant type, amount, and added timing were important parameters for increasing final purification yield. Finally, Sato and Nomura confirmed that the purified structure retained the ability to bind lipid vesicle surface.
The method developed by Sato and Nomura is based on a simple approach of adding surfactant under appropriate conditions. Therefore, this method can be combined with other conventional purification methods, not limited to the electrophoresis-based method.
"We believe that such purified hydrophobic DNA nanostructures will be useful for the construction of artificial cells and molecular robots that exhibit complex functions by using functionalized lipid membranes with DNA nanostructures," say Sato and Nomura.
The research team will next work on implementing molecular communication function on molecular robots through selective molecular transport and connecting multiple lipid vesicles.
More information: Shoji Iwabuchi et al, Surfactant‐Assisted Purification of Hydrophobic DNA Nanostructures, ChemBioChem (2022). DOI: 10.1002/cbic.202200568
Journal information: ChemBioChem
Provided by Kyutech