This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
What crocodile DNA reveals about the Ice Age
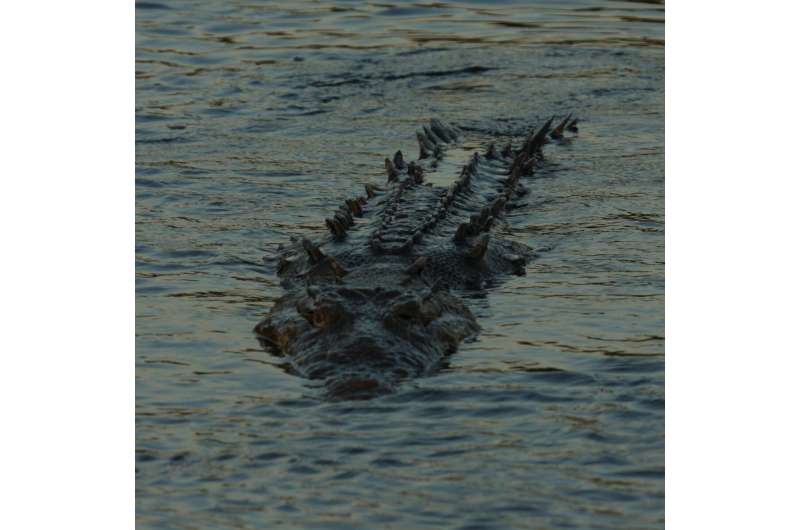

What drives crocodile evolution? Is climate a major factor or changes in sea levels? Determined to find answers to these questions, researchers from McGill University discovered that while changing temperatures and rainfall had little impact on the crocodiles' gene flow over the past three million years, changes to sea levels during the Ice Age had a different effect.
"The American crocodile tolerates huge variations in temperature and rainfall. But about 20,000 years ago—when much of the world's water was frozen, forming the vast ice sheets of the last glacial maximum—sea levels dropped by more than 100 meters. This created a geographical barrier that separated the gene flow of crocodiles in Panama," says postdoctoral fellow José Avila-Cervantes, working under the supervision of McGill professor Hans Larsson.
The researchers point out that the crocodiles are good swimmers, but they can't travel long distances on land. As a result, the Caribbean and Pacific crocodile populations were isolated from each other, and consequently have undergone different genetic mutations.
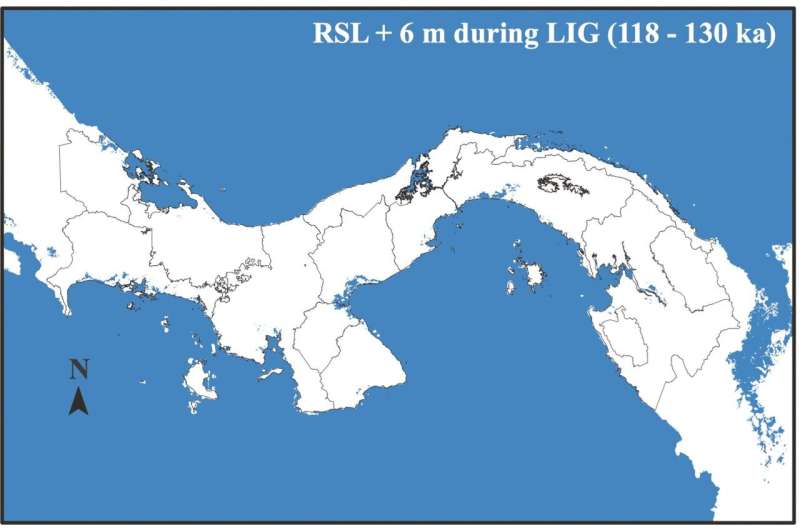
The team compared the climate tolerance of living populations of American crocodiles (Crocodylus acutus) to the paleoclimate estimates for the region over the past 3 million years—the time span of extreme climate variation during the Ice Age.
"This is one of the first times Ice Age effects have been found in a tropical species. It's exciting to discover effects of the last Ice Age glaciation still resonate in the genomes of Pacific and Caribbean American crocodiles today," says Larsson, Professor of Biology at the Redpath Museum of McGill University.
"Discovering that these animals would have easily tolerated the climate swings of the Ice Age speaks to their resilience over geological time. Only humans in recent decades of hunting and land development seem to really affect crocodiles," he says. The findings offer new insight into how environmental drivers affect genetic evolution and where conservation efforts of particular crocodile populations in Panama should be focused.
The paper is published in the journal Evolution.
More information: Jose Avila-Cervantes et al, Ice Age effects on genetic divergence of the American crocodile (Crocodylus acutus) in Panama: reconstructing limits of gene flow and environmental ranges: A reply to O'Dea et al., Evolution (2023). DOI: 10.1093/evolut/qpac006
Journal information: Evolution
Provided by McGill University