Tracing the rapid evolution of spermatogenesis across mammals
Evolutionary pressure across male mammals to guarantee the procreation of their own offspring led to a rapid evolution of the testicle. Bioinformatic studies—conducted by an international team of researchers led by Prof. Dr. Henrik Kaessmann from the Center for Molecular Biology of Heidelberg University—show that this pressure particularly accelerated the evolution of later stages of sperm formation.
The aim of these contrastive studies was, for the first time, to decode the genetic regulation of sperm formation in various species of mammals and in human beings, thereby tracing the evolution of this spermatogenesis. At the same time, the researchers were also able to detect genes whose activity had remained unchanged in the course of evolution.
Spermatogenesis in the testicle is controlled by a finely coordinated, complex interplay of the activity of different genes—also known as gene expression. Hitherto the understanding of these genetic programs had been largely confined to the mouse. "Consequently little was known about the genetic foundations that constitute the big differences in spermatogenesis across different mammals, both with regard to the number of sperm cells formed and also to their properties," explains Noe Mbengue, a doctoral researcher in Prof. Kaessmann's group "Evolution of the mammalian genome."
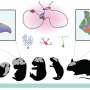
The Heidelberg scientists have now succeeded in defining the expression of all genes at the level of individual cells during the whole of spermatogenesis for ten different mammals. The organisms they studied represent all major groups of mammals and include humans as well as their closest relatives, great apes. To do this, the researchers used state-of-the-art single-cell genomics technologies.
Based on this data they were subsequently able to trace the evolution of spermatogenesis with the aid of bioinformatic comparisons between the different mammals. According to Prof. Kaessmann, these comparative studies uncovered a time-related pattern.
"While the genetic programs in the early stages of spermatogenesis are very similar among mammals, in later stages they differ greatly; that means that the rapid evolution of the testicle is a result of major differences in cells during late spermatogenesis," says Dr. Florent Murat, a former postdoc in Henrik Kaessmann's research group and now a group leader at the National Research Institute for Agriculture, Food and Environment (INRAE) in Rennes (France).
Further analyses by the scientists revealed genes whose activity had remained unchanged in the course of evolution. They regulate fundamental processes of sperm cell formation that are the same for all mammals. "Hence our data also supplies valuable elements for researching fertility disorders in men," Prof. Kaessmann explains.
Finally, the scientists' data enabled them for the first time to distinguish sperm cells that carry either an X or a Y chromosome and thus determine the sex of the offspring. With the aid of this division, the researchers succeeded in systematically studying the gene expression on these sex chromosomes. As these investigations showed, gene expression on the sex chromosomes of all male mammals is downregulated during the maturation division known as meiosis. This mechanism is presumably fundamental for preventing a disadvantageous genetic exchange between the X and Y chromosome during meiosis.
The results of the study on the evolution of spermatogenesis across mammals were published in the journal Nature.
More information: Henrik Kaessmann, The molecular evolution of spermatogenesis across mammals, Nature (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-05547-7. www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-05547-7
Journal information: Nature
Provided by Heidelberg University