An environmentally friendly RNA-based spray to help combat rust disease in plants
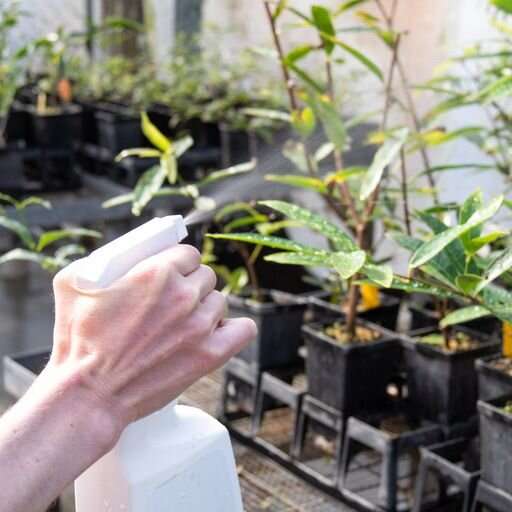

University of Queensland scientists have developed an environmentally friendly RNA-based spray to help combat myrtle rust, which has wiped out many Australian plants.
Developed in collaboration with Department of Agriculture and Fisheries forest pathologists, the spray induces RNA interference (RNAi)—a natural way to shut down protein translation—which means it could stop the spread of myrtle rust through bushland, home gardens and nurseries.
Ph.D. candidate Rebecca Degnan said in the decade myrtle rust had been in Australia it had become a huge problem, with more than 350 native hosts.
"Of those plants that have been screened, only three percent were completely unable to be infected, and more than 40 species have been deemed conservation priorities because of damage from myrtle rust," Ms. Degnan said.
Molecular plant biologist Dr. Anne Sawyer said the team wanted to find an alternative myrtle rust control to fungicides.
"Growers rely heavily on fungicides, but they come with a lot of problems such as being harmful to humans and beneficial organisms like bees and monarch butterflies as well as water contamination," Dr. Sawyer said.
"Pests and pathogens can also develop resistance to chemicals and consumers are becoming more aware of residues on their fruit and vegetables.
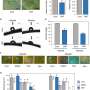
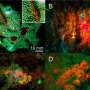
"We already knew that RNA interference works against other plant pests and pathogens, and our research found rusts are very amenable to this method when we sprayed the double-stranded RNA onto the plants."
Dr. Sawyer said the early results were very positive, and further research would test the spray in more uncontrolled conditions outside of the lab and glasshouse.
"Now that we've seen the proof of concept of RNAi in myrtle rust, there are a lot of possibilities for other rusts as well," Dr. Sawyer said.
"It's really exciting, especially when you talk to people who have been working on myrtle rust for a long time and have seen the damage it can do."
The research is published in Molecular Plant Pathology.
More information: Rebecca M. Degnan et al, Exogenous double‐stranded RNA inhibits the infection physiology of rust fungi to reduce symptoms in planta, Molecular Plant Pathology (2022). DOI: 10.1111/mpp.13286
Journal information: Molecular Plant Pathology
Provided by University of Queensland