When mothers shut down the fathers' genes in plant embryos
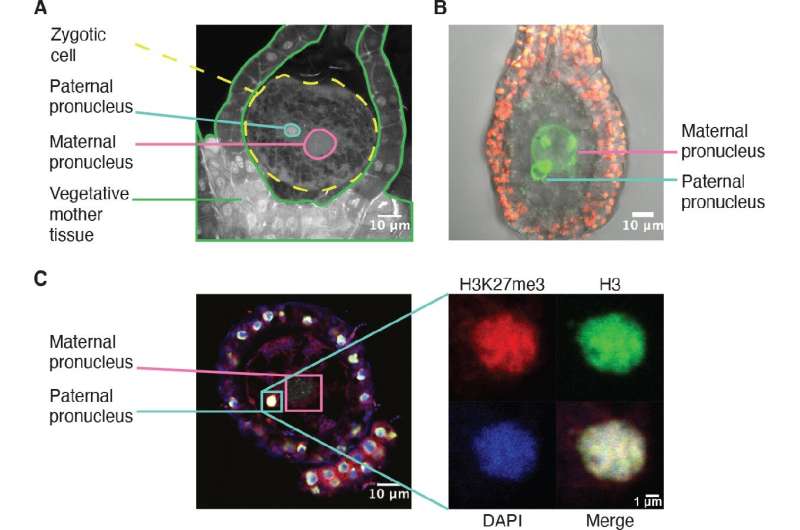
In humans, and many other species, both genes inherited from the mother and from the father influence how embryos develop. In the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha, however, the mother has total control, as researchers from the Berger lab at GMI now uncovered. In a study published in eLife, the researchers show that the "mother plant" has total control and completely inactivates the paternal genes in its embryos to ensure they develop properly.
Humans have two sets of chromosomes, one maternal and one paternal, and both usually contribute traits to the individual, depending on which genes are expressed—this is what makes us "diploids." But that's not the case for all living beings:
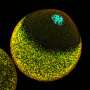
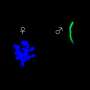
Algae and relatives of mosses, including the liverworts, spend most of their life cycle with just a single set of chromosomes. The liverwort only has a short diploid phase when the genetic material of one maternal and one paternal germ cell combine to give rise to an embryo, carried within the maternal tissue. In this short phase as a diploid, the plant needs to have a mechanism in place to cope with the doubling of its genetic material.
One such mechanism is the silencing of one copy of a gene, also called "parental genomic imprinting." With genomic imprinting, even a whole chromosome can be permanently inactivated, as is the case for one of the two X chromosomes in women. "Parental genomic imprinting had been identified only in species that innovated extraembryonic tissues that channel nutrients from the mother to the embryo, like the placenta in mammals and the endosperm in flowering plants," says Frédéric Berger, Senior Group Leader at GMI—Gregor Mendel Institute of Molecular Plant Biology of the Austrian Academy of Sciences.
A genomic coping mechanism led by the maternal genes
The liverwort embryos also grow within the maternal tissues, but unlike mammals, their development does not involve extraembryonic tissues. With these factors in mind, the Berger research group set out to investigate the existence of parental genomic imprinting mechanisms in Marchantia.
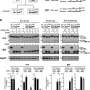
"We found that Marchantia completely inactivates the paternal chromosomes in the embryo, even before the fusion of the paternal and maternal genomes. This way, Marchantia maintains a functional haploidy even during the short stage in which it becomes diploidic," says first author Sean Montgomery, a recent Ph.D. graduate from the Berger lab at GMI. The team also found that the molecular mark deposited on the entirety of the paternal chromosomes is maintained throughout the development of the embryo. "Hence, the embryo development depends solely on the expression of the maternal genes. In a way, the maternal genes have total control. Disrupting this process leads to the expression of the paternal genes and the death of the embryo," explains Berger.
Scratching the surface of nature's diversity
The silencing mechanism that the team described in the liverwort is itself not new. This targeted silencing is mediated by the Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2). However, this precise mechanism had not yet been associated with the silencing of whole chromosomes.
As ancestors of the liverwort are considerably older than those of mammals or flowering plants, the findings suggest that imprinting mechanisms evolved much earlier than is currently known. In addition, Berger and his team propose that this phenomenon has evolved multiple times in various life forms and that many imprinting mechanisms remain to be discovered. "With our work, we were able to highlight a unique aspect of biology, a slice of nature's broad diversity," concludes Montgomery.
More information: Sean Akira Montgomery et al, Polycomb-mediated repression of paternal chromosomes maintains haploid dosage in diploid embryos of Marchantia, eLife (2022). DOI: 10.7554/eLife.79258
Journal information: eLife
Provided by Gregor Mendel Institut für Molekulare Pflanzenbiologie (GMI)