Mechanism of bacterial toxins in deadly attacks
Only one thousandth of a milligram of the bacterial botulinum toxin is necessary to kill a living organism. The toxin unfolds its lethal effect by preventing the release of neurotransmitters at the point where nerve cells attach to muscles, thereby paralyzing them. As simple as it may seem, this process is in fact a sophisticated and multi-staged procedure. No less complex and in fact very effective is the intoxication process of toxin complexes (Tc), virulence factors of many bacteria, including insect and human pathogens.
A bacterial syringe delivers a deadly enzyme
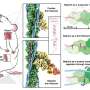
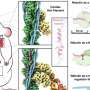
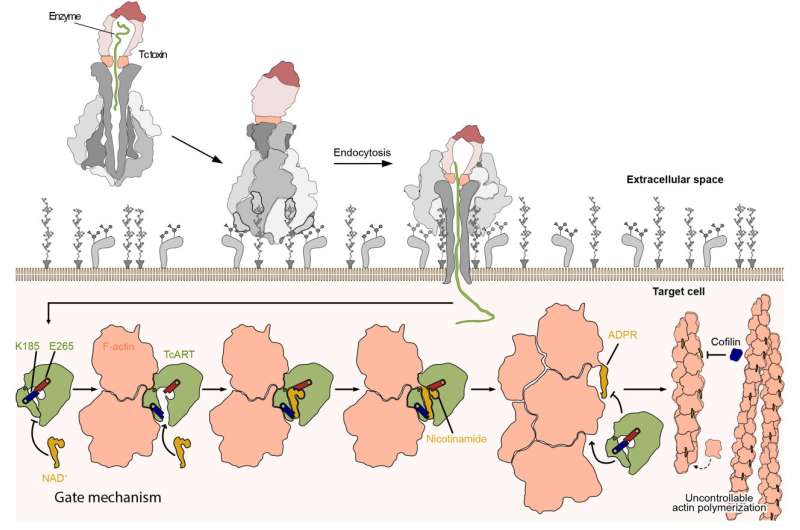
The mechanism of action of Tc toxins has only recently been uncovered to a greater extent by the work of Stefan Raunser's team in structural biology at the MPI Dortmund. "Unraveling the structure of the Tc toxin subunits and their assembly by cryo electron microscopy (cryo-EM) enabled us to understand the key steps of toxin activation and membrane penetration," says Raunser. The scientists showed that the subunits of the Tc toxin complex work together like a syringe (link to former press release)): once the subunits are assembled, structural changes in the complex trigger the opening of a cocoon which contains a toxic enzyme, which is then secreted in a unique injection mechanism via a channel into the host cell (link). There, it unfolds its deadly effect by disturbing the regulation of the cell's cytoskeleton, which consists of a network of polymerized actin (F-actin) filaments involved in many essential cellular processes.
Setting up the opponent by reducing the striking distance
"For a long time, we struggled with obtaining a complete picture of the intoxication process, since we lacked the structural data of the secreted enzymes, one of which is TccC3," reflects Raunser. Until recently, it was only known that TccC3 transfers an ADP-ribose group to actin promoting its aberrant polymerization, which leads to actin filament clumping. "TccC3 is what we call a "difficult" system for structural investigations due to its size and high flexibility," says Hartmut Oschkinat. "Only by applying solution NMR, could we overcome this challenge and visualize the protein's 3D structure for the first time." By fusing two further cryo-EM snapshots of TccC3 bound to F-actin and of the modified F-actin alone, the scientists have uncovered the enzyme's unique mechanism of action. "TccC3 acts like a boxer who sets up his opponent to make him vulnerable to the attack," says Stefan Raunser. In the first step, the enzyme binds to a region between two consecutive actin subunits of F-actin. TccC3 then opens a gate, which brings the molecule NAD+ that contains the ADP-ribose group within striking distance to a reactive site on actin. Once the bulky ADP-ribose group is transferred to F-actin, it is no longer accessible for its depolymerizing factors, whereby F-actin can no longer be broken down and thus clumps.
In addition to this discovery, the scientists' findings have helped formulate an explanation for the strikingly high efficiency of the enzyme. When the enzyme detaches from F-actin, its gate mechanism prevents a futile rebinding to the already modified actin as preparation for the next attack. "It is amazing how all these mechanisms evolved to increase the toxins potency to the max. And nature did quite a good job since botulinum toxins, ricin and other biotoxins are still considered the most toxic substances known," Raunser concludes.
The research was published in Nature Communications.
More information: Alexander Belyy et al, Mechanism of threonine ADP-ribosylation of F-actin by a Tc toxin, Nature Communications (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-31836-w
Provided by Max Planck Society