What's dynamic pricing? An operations management scholar explains
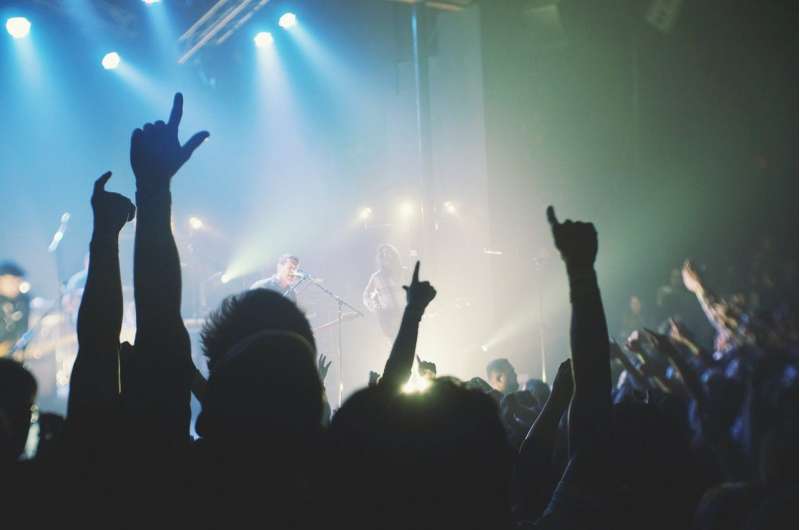

Whether you're booking a plane ticket at the last minute or looking to go to a lackluster preseason football game, you might encounter what's known as dynamic pricing.
Using this strategy, companies adjust what they are charging in response to demand. They can cut or raise the prices as high as the market will bear in real time to maximize the money they make through sales.
In addition to airlines and sports teams, hotel chains, car rental companies, ride-sharing platforms, entertainment companies, cruise lines and any retailers selling seasonal goods or hot items use dynamic pricing.
It uses specialized software and sophisticated algorithms to closely monitor the remaining number of products available, along with how much time remains before item must be sold or wasted. Prices get adjusted accordingly.
Why dynamic pricing matters
Sports and entertainment industries have a big incentive to use dynamic pricing.
Since tickets to sports and entertainment events can be resold, any gap between their face value and what fans are willing to pay leads to openings in the market for brokers.
For popular events such as playoff games or once-a-decade tours, technologically advanced brokers can snap up large numbers of tickets from the original seller and resell them with huge markups that don't benefit the sports teams, artists or venues.
When a team, an entertainment company or a vendor they have hired uses dynamic pricing, at least ideally, more ticket revenue flows into the pockets of the people responsible for the events. That is, if concertgoers will ultimately pay $249 to see Taylor Swift perform, it makes more sense for them to pay an official vendor that sum, not a scalper who paid $75 for tickets they never intended to use.
Springsteen ticket outcry
To maximize the money made through sales, dynamic pricing makes sense. However, fair treatment is an important factor in pricing decisions since customers don't want to be exploited. That is probably why sports teams and entertainment companies have been reluctant to set prices at sky-high levels that might harm their reputations.
When dynamic pricing results in people feeling gouged, a public outcry can ensue. A good example occurred in the summer of 2022 when Ticketmaster, the leading U.S. ticket seller and distributor, charged fans $5,000 apiece or more for some of the best seats for Bruce Springsteen's 2023 tour.
The company's response generated a new round of buzz with its matter-of-fact tone and lack of an apology. "Prices and formats are consistent with industry standards for top performers," Ticketmaster said.
Provided by The Conversation
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.![]()