Compound found in trees has potential to kill drug-resistant bacteria
University of Portsmouth researchers have found a naturally occurring compound, known as hydroquinine, has bacterial killing activity against several microorganisms.
Antimicrobial resistance has become one of the greatest threats to public health globally. It occurs when bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites change over time and no longer respond to medicines, making it difficult to treat infections. Because of this, there is a pressing need for the development of new antimicrobial drugs to combat infections.
A new study by scientists from the University of Portsmouth and Naresuan and Pibulsongkram Rajabhat Universities in Thailand explored whether hydroquinine, which is found in the bark of some trees, could inhibit any bacterial strains. Hydroquinine is already known to be an effective agent against malaria in humans, but until now there has been little investigation into its drug-resistant properties.
The findings, published in the Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease journal, suggest the antimicrobial properties of the organic compound make it a potential candidate for future clinical investigation.
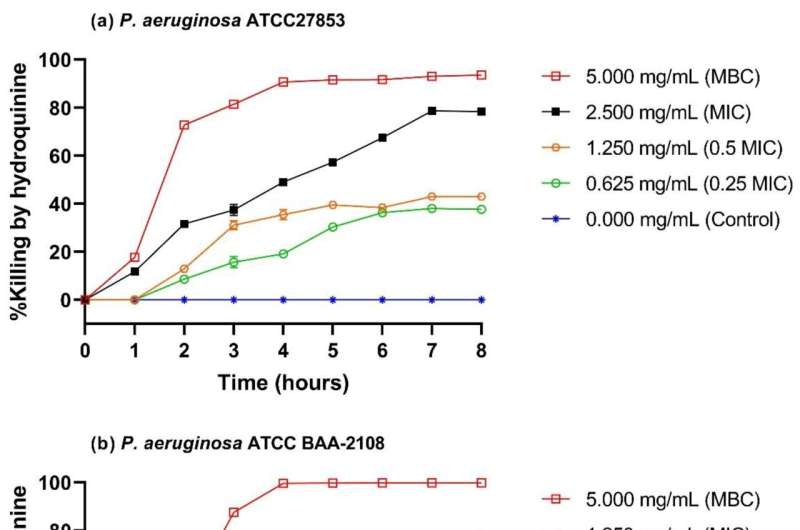
Dr. Robert Baldock from the School of Pharmacy and Biomedical Sciences at the University of Portsmouth, said, "Using bacterial killing experiments, we found that hydroquinine was able to kill several microorganisms including the common multidrug-resistant pathogen pseudomonas aeruginosa.
"Characteristically, we also discovered that one of the main mechanisms used by these bacteria to escape killing activity of the drug was upregulated with treatment—indicating a robust response from the bacteria.
"By studying this compound further, our hope is that it may in future offer another line of treatment in combatting bacterial infections."
Drug-resistant bacteria occur in more than 2.8 million infections and are responsible for 35,000 deaths per year. Common antibiotic-resistant "superbugs" cause diseases including sepsis, urinary tract infections, and pneumonia. Statistics show bloodstream infections with the bacteria—P. aeruginosa are associated with high mortality rates of between 30 and 50%.
The study recommends further investigation into the antimicrobial resistance properties and side effects of hydroquinine.
Dr. Jirapas Jongjitwimol from the Department of Medical Technology at Naresuan University added, "Our future research aims to uncover the molecular target of hydroquinine. This would help our understanding of how the compound works against pathogenic bacteria and how it could potentially be used in a clinical setting."
More information: Nontaporn Rattanachak et al, Hydroquinine Possesses Antibacterial Activity, and at Half the MIC, Induces the Overexpression of RND-Type Efflux Pumps Using Multiplex Digital PCR in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease (2022). DOI: 10.3390/tropicalmed7080156
Provided by University of Portsmouth