Analyses of heat shock transcription factors and database construction based on whole-genome genes in plants

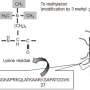
The heat shock transcription factors (Hsfs) are members of a key transcription factor gene family that responds to heat stress and plays an important role in heat resistance. Previous reports have shown that Hsf family genes contain several conserved domains. At the N terminus is a DNA-binding domain (DBD) that can recognize promoter elements of heat-responsive genes. An adjacent oligomerization domain (OD or HR-A/B) is found in all Hsf family genes and comprises mainly hydrophobic heptad repeats. HSFs are sequence-specific DNA binding proteins that bind specifically to heat-shock elements (HSEs) with high affinity.
The activation of HSFs and their subsequent binding to HSEs are key steps in regulating the expression of almost all heat shock genes. Until now, the Hsf gene family has been characterized in whole genomes of many plant species, including Arabidopsis thaliana (21 genes), Oryza sativa (25), Solanum lycopersicum, and others. However, no database has previously been created specifically for the Hsf gene family, and some detailed information on this family is still absent.
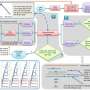
Recently, scientists from the North China University of Science and Technology constructed an Hsf database from which researchers can retrieve information on Hsf family genes in order to explore their expression patterns and evolutionary mechanisms. They identified 2,950 Hsf family genes from 111 horticultural species and other representative plants. A phylogenetic tree of all the Hsf genes was constructed, which indicated that the Hsf genes of each branch had evolved independently after species differentiation.
The evolutionary trajectories of Hsf genes were also uncovered by motif analysis, and a heat response network was constructed using 24 Hsf genes and 2421 downstream and 222 upstream genes from A. thaliana. Further analysis showed that Hsf genes and other transcription factors interacted with one another during the heat stress response. Syntenic and phylogenetic analyses were performed using Hsf genes from A. thaliana and a pan-genome from 18 Brassica rapa accessions. The researchers also performed expression pattern analysis of Hsf and six Hsp family genes using expression values from different tissues and heat treatments in B. rapa. An interaction network was constructed among Hsf and Hsp gene families from B. rapa, and several core genes were identified in the network.
"We performed comprehensive analyses of the Hsf gene family in 111 horticultural and other representative plants, especially for the study of the horticultural plant B. rapa. We also constructed a database for all identified Hsf family genes," Dr. Song said. This study will serve as a useful resource for future studies on the biological functions and evolutionary history of the Hsf gene family.
The research was published in Horticulture Research.
More information: Tong Yu et al, Large-scale analyses of heat shock transcription factors and database construction based on whole-genome genes in horticultural and representative plants, Horticulture Research (2022). DOI: 10.1093/hr/uhac035
HSF Database: hsfdb.bio2db.com
Provided by Nanjing Agricultural University The Academy of Science