Modeling high-harmonic generation without resorting to perturbation theory
An advanced mathematical model that can describe high-energy interactions between light and matter has been developed by two RIKEN researchers and a collaborator. The approach could be extended to offer new insights in other areas of physics.
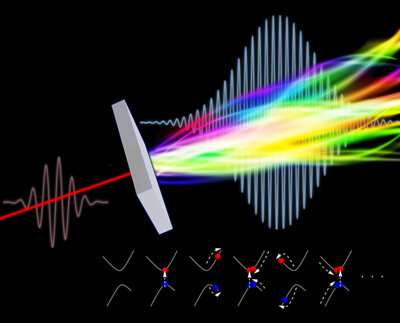
High-harmonic generation is a powerful technique that converts laser light from one wavelength, or color, to another (Fig. 1). Put simply, it converts a low-energy, long-wavelength photon into multiple higher energy, shorter wavelength photons.
High-harmonic generation has several applications. For example, it offers a way to create table-top sources of extreme ultraviolet or X-ray light using lasers, rather than expensive synchrotron facilities. High-harmonic generation can also produce ultrashort light pulses, as short as one attosecond (10−18 second) or maybe even one zeptosecond (10−21 second), which are useful for imaging extremely rapid processes such as those that occur in atoms. But high-harmonic generation is inherently difficult to model mathematically, and thus understand fully.
Now, Hidetoshi Taya and Masaru Hongo from the RIKEN Interdisciplinary Theoretical and Mathematical Sciences (iTHEMS) Program, together with their colleague Tatsuhiko Ikeda from the University of Tokyo, have developed an analytical approach to high-harmonic generation in the so-called non-perturbative regime for the first time.
Perturbation theory is a powerful mathematical tool that starts with a simplified, but mathematically solvable, version of a problem. It then adds small variations, or perturbations, to achieve a more accurate answer.
However, not all processes are amenable to perturbation theory. "Many physical phenomena can't be analyzed using the standard perturbative approach," says Taya. "Thus, establishing theoretical approaches for non-perturbative regimes is one of the biggest challenges in theoretical physics."
Taya, Hongo and Ikeda used mathematical techniques that had not previously been applied to high-harmonic generation. Their approach revealed the microscopic mechanism that converts incoming intense light into high harmonics, and enabled any experimental observable to be calculated with just a pen and paper—no need for computers.
This research could help shed light on several intriguing experimental results that have features not exhibited by high-harmonic generation in the perturbative regime.
The same mathematical tool could also be useful in other areas of physics. "I'm particularly interested in application to the physics of high-energy particles," says Taya. "For example, our theory can be applied to quantum electrodynamics—the fundamental theory for electrons and photons. It predicts that high-harmonic generation will occur not only in materials but also in a vacuum—an interesting possibility that could be tested with future intense laser facilities."
More information: Hidetoshi Taya et al, Analytical WKB theory for high-harmonic generation and its application to massive Dirac electrons, Physical Review B (2021). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.104.L140305
Journal information: Physical Review B
Provided by RIKEN