Examining how the superbug Pseudomonas aeruginosa reacts to antibiotics
Researchers at Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) have studied how different drugs affect the difficult-to-treat bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa. According to the World Health Organisation, new treatment options for the pathogen are urgently required, as some strains are already resistant to all currently approved antibiotics. The Bochum-based team headed by Professor Julia Bandow exposed P. aeruginosa to various substances and observed their effects on the protein make-up of the bacteria, also known as the proteome. The results enable the researchers to conclude what makes P. aeruginosa resistant; in addition, new approaches for treatment of the priority pathogen were investigated. Together with the group of Professor Pei Zhou from Duke University in the USA, the RUB team describes the analyses in Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy.
Bacteria are often categorized as either Gram-positive or Gram-negative depending on how they react in a certain staining procedure, namely the Gram stain. "Infections with the Gram-negative pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa are feared as being difficult to treat," says Julia Bandow, head of the Applied Microbiology research group at RUB. Patients can become infected with the germ in hospitals, for example; it causes pneumonia or sepsis, which can be fatal.
Specific properties might become targets for drugs
Gram-negative bacteria have a number of properties that are different from those of Gram-positive bacteria. For example, they produce sugar-lipid compounds that are characteristic for their outer membranes. "Some of the specific properties of Gram-negative bacteria could provide attractive targets for antibiotics," says Bandow. "This is what we seek to exploit."
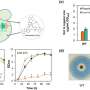
In the first step, the researchers investigated why P. aeruginosa is resistant to so many common antibiotics. They treated the germ with twelve different approved antibiotics and documented the resulting changes in the proteome. This allowed them to deduce how the cells defend themselves against the antibiotics. The team also divided the individual substances into groups based on how similar the triggered effects were. This correlated with similarities in the compounds' modes of action.
Furthermore, the scientists tested the experimental substance CHIR-090. Compared to the effects of approved antibiotics, CHIR-090 produced a unique proteome response. CHIR-090 blocks the production of sugar-lipid compounds addressing a target that has not yet been exploited clinically. No resistance to the drug has been observed in clinically relevant bacterial strains. "Resistance to new classes of substances is expected to emerge more slowly than to derivatives of conventional antibiotics," explains Julia Bandow.
More information: Dominik Wüllner et al, Adaptive responses of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to treatment with antibiotics, Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (2021). DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00878-21
Journal information: Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy
Provided by Ruhr-Universitaet-Bochum