Breaking down glycosides in the gut and in nature
Rarely does a tool become more useful when it's broken, but that's just the case with C-glycoside, a molecule found in many plants, foods, and medicines. To be used by the body, C-glycosides must be broken down. Researchers in Japan have uncovered new insights into how this process occurs.
In a study published in Nature Communications, researchers from University of Tsukuba have shed new light on the mechanism involved in the metabolism of C-glycosides, which contain a sugar group that is attached via a carbon-carbon (C-C) bond.
Humans regularly ingest C-glycosides found in fruits and vegetables. Breakdown of C-glycosides via the cleavage of the C-C bond occurs in the large intestine and is necessary for the body to utilize these molecules. However, the catalytic mechanisms involved in this process are not fully understood. Researchers at University of Tsukuba investigated the mechanism and components involved in C-glycoside metabolism in the human body and in nature.
"Using assimilation screening and genome mining, we were able to identify multiple C-glycoside deglycosylation enzymes present in intestinal bacteria and soil bacteria," says senior author Michihiko Kobayashi.
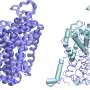
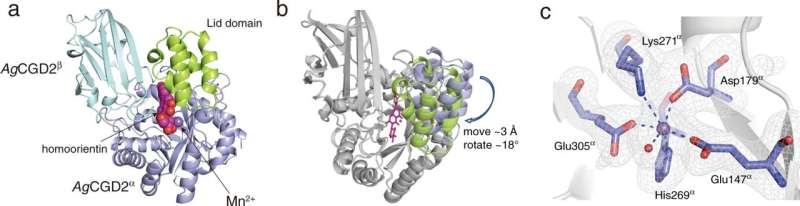
The research team used biochemical techniques to identify the role and specificity of C-glycoside deglycosylation enzymes (CGDs) in the metabolism of C-glycosides. Structural analysis revealed the unique structures of the CGDs from the gut and soil bacteria and illustrated the relationship between the enzyme structure and function.
"We found that the CGDs from both intestinal and soil bacteria functioned as catalysts for selective C-C bond cleavage reactions," explains author Takuto Kumano. "Per our analyses, we propose a C-C bond cleavage mechanism involving acid/base catalysis in the breakdown of C-glycosides."
The researchers observed that the structure of CGDs in intestinal bacteria differed from that of CGDs in soil bacteria. However, the nature of the reaction for C-glycoside metabolism appeared to be common in soil and intestinal microorganisms.
Glycosides occur throughout nature and are present in certain medicines that treat, for example, heart failure. Further understanding of the enzymes involved in C-glycoside metabolism will provide more insight into how the body breaks down these molecules for use and how this process may be used for the activation of drugs containing C-glycosides.
More information: Takahiro Mori et al, C-Glycoside metabolism in the gut and in nature: Identification, characterization, structural analyses and distribution of C-C bond-cleaving enzymes, Nature Communications (2021). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-26585-1
Journal information: Nature Communications
Provided by University of Tsukuba