Aerosol formation in clouds: Studying climate modeling's last great uncertainty factor

Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have studied for the first time how chemical reactions in clouds can influence the global climate. They found that isoprene, the dominant non-methane organic compound emitted into the atmosphere, can strongly contribute to the formation of organic aerosols in clouds. They published their results today in the journal Science Advances.
Aerosols, a mixture of solid or liquid particles suspended in the air, play an important role in Earth's climate. Aerosols originate either from natural or human sources. They influence Earth's radiation balance by interacting with sunlight and forming clouds. However, their effect remains the single most significant uncertainty in climate models.
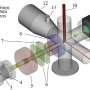
One substance that is very common in the atmosphere is isoprene, an organic compound whose reactions in the gas phase are relatively well understood. Isoprene is given off by trees and can produce aerosols when it is oxidized. How isoprene and its reaction products react in cloud droplets is still largely unknown. That's why researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have used a type of flow reactor with wetted walls, together with the most advanced mass spectrometers, to investigate what could be happening chemically inside clouds for the first time under atmospherically relevant conditions.
"Our experimental setup allows us for the first time to precisely investigate the distribution of organic vapors at the air-water interface under near-environmental conditions," says Houssni Lamkaddam, a researcher in the Laboratory of Atmospheric Chemistry at PSI. "With our apparatus, we can now simulate what happens in clouds."
-
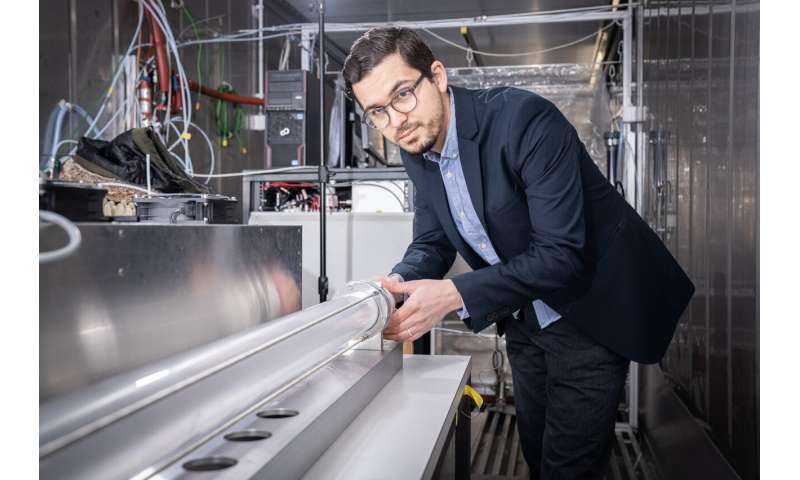

Houssni Lamkaddam, researcher at Atmospheric Chemistry Laboratory of PSI, at the experimental apparatus. Credit: Paul Scherrer Institute/Mahir Dzambegovic -
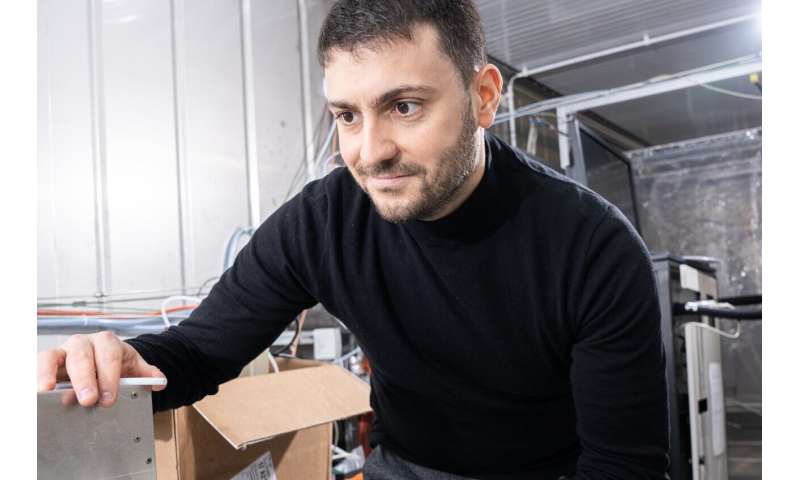

Imad El Haddad, head of the Molecular Cluster and Particle Processes group and one of the authors of the study. Credit: Paul Scherrer Institute/Mahir Dzambegovic
What exactly happens in clouds?
In the special apparatus, a so-called wetting reactor, a thin film of water is maintained on the inside of a quartz tube. A gas mixture containing, among other substances, isoprene, ozone, and so-called hydroxyl radicals is fed into the glass cylinder. UV lamps are installed around the glass cylinder to simulate daylight conditions for some of the experiments.
Using this setup, the researchers found that up to 70% of the isoprene oxidation products can be dissolved in the water film. The subsequent aqueous oxidation of the dissolved species produces substantial amounts of secondary organic aerosols. On the basis of these analyzes, they calculated that the chemical reactions that take place in clouds are responsible for up to 20% of the secondary organic aerosols on a global scale.
"This is another important contribution to a better understanding of the processes in the atmosphere," sums up Urs Baltensperger, scientific head of the Laboratory of Atmospheric Chemistry at PSI. Earth's radiation balance is a very important factor in the entire climate process and thus also in climate change. "And aerosols play a crucial role in this," says the atmospheric scientist. While aerosols form cloud droplets, this research shows that clouds can also form aerosols through the aqueous chemistry of organic vapors, a process that is well known with regard to sulfate aerosols but here is also shown for the organic fraction. This new experimental setup, developed at PSI, opens up the possibility of investigating aerosol formation in clouds under near-atmospheric conditions so that these processes can ultimately be included in climate models.
More information: DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abe2952 H. Lamkaddam el al., "Large contribution to secondary organic aerosol from isoprene cloud chemistry," Science Advances (2021). advances.sciencemag.org/lookup … .1126/sciadv.abe2952
Journal information: Science Advances
Provided by Paul Scherrer Institute