Glass blowing inspires new class of quantum sensors

When Adelaide glass blower Karen Cunningham made art using diamond and glass she had no idea it would inspire a new kind of hybrid material. Now a consortium of scientists, including from RMIT University and University of Adelaide, is using the technology to make a new class of quantum sensors.
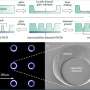
The study published in APL Materials reveals how high-performance diamond sensors can be made using conventional glass fibers.
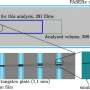
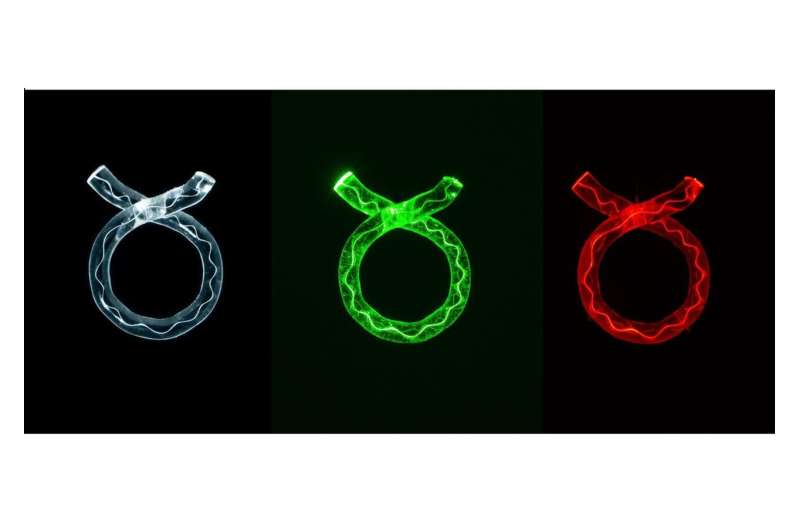
By embedding micron-scale diamond particles within the cross section of a silicate glass fiber, the team has demonstrated the use of a robust fiber material capable of sensing magnetic fields.
Study lead author and RMIT School of Science's Dr. Dongbi Bai said it was an exciting achievement that opened the door to many applications in underwater monitoring, mining and beyond.
"This allows us to make cheap quantum sensor networks that are able to monitor changes in magnetic field, with many useful applications and the answers to questions we haven't thought of yet," she said.
Diamond is one of the front runner technologies for quantum magnetic field sensing, with applications as diverse as brain scanning, navigation and mineral exploration.
But, diamond particles need to be viewed through high-end microscopes that aren't suited for use over an extended period or in the field.
University of Adelaide Deputy Director of the Institute for Photonics and Advanced Sensing, Heike Ebendorff-Heidepriem, said the team had been working to get around this issue for a decade.
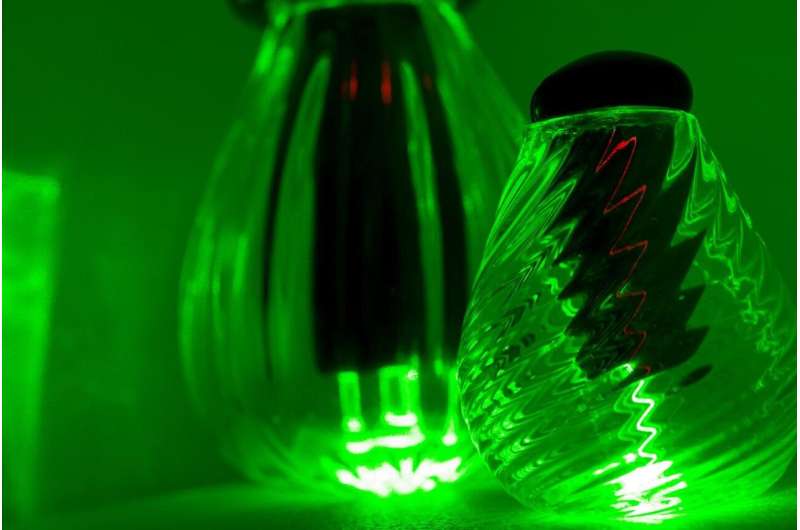

"But because diamond burns at high temperatures, we've been limited in the glasses that we can use," she added.
The team has learnt a lot from these so-called 'soft glasses,' but these glasses are non-standard and not as good at guiding light as conventional silica fibers, such as those used in the National Broadband Network.
From art to science
This is where glass artist Karen Cunningham comes into the picture. She was making art using nanoparticles to show how light moves through glass and was fascinated by the diamonds that were used by Heike and her colleagues in her research.
"We gave Karen some of our larger diamonds to see how they worked," RMIT School of Science's Professor Brant Gibson, explained.
The diamonds he gave Karen were around one micron in diameter, which is 50 times smaller than the width of a human hair.

"For most of our work, these diamonds are just too big, so we use them mainly for testing," he said.
Incredibly, the diamonds survived Karen's glass blowing, and were part of her exhibition at JamFactory in Adelaide, in 2017.
"For us, it was the lightbulb moment and we knew we could make diamond sensors in more conventional glass fibers," Heike said.
To go from Karen's art to prototype sensors took another three years of testing and fabrication, explained Dr. Dongbi Bai.
"It always takes hard work to go from the idea to the product, but I'm so excited by what we've achieved, and even more excited by where this new quantum sensor can take us," she said.
More information: D. Bai et al, Fluorescent diamond microparticle doped glass fiber for magnetic field sensing, APL Materials (2020). DOI: 10.1063/5.0013473
Provided by RMIT University