Simple method for ceramic-based flexible electrolyte sheets for lithium metal batteries

Researchers at Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a new method to make ceramic-based flexible electrolyte sheets for lithium metal batteries. They combined a garnet-type ceramic, a polymer binder and an ionic liquid, producing a quasi-solid-state sheet electrolyte. The synthesis is carried out at room temperature, requiring significantly less energy than existing high-temperature (> 1000°C) processes. It functions over a wide range of temperatures, making it a promising electrolyte for batteries e.g., in electric vehicles.
Fossil fuels account for most of the world's energy needs, including electricity. But fossil fuels are running out, and burning them also leads to the direct emission of carbon dioxide and other pollutants like toxic nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere. There is a global demand to shift to cleaner renewable energy sources. But major sources of renewable energy like wind and solar power are often intermittent—the wind does not blow all the time and the sun does not shine at night. Advanced energy storage systems are thus required to use renewable, intermittent sources more effectively. Lithium ion batteries have had a profound impact on modern society, powering a wide range of portable electronics and appliances like cordless vacuum cleaners since their commercialization by Sony in 1991. But using these batteries in electric vehicles (EVs) still requires a substantial improvement in the capacity and safety of state-of-the-art Li-ion technology.
This has led to a renaissance of research interest in lithium metal batteries: Lithium metal anodes have a much higher theoretical capacity than the graphite anodes in commercial use now. There are still technological hurdles associated with lithium metal anodes. In liquid-based batteries, for example, lithium dendrites (or arms) can grow which might short-circuit the battery and even lead to fires and explosions. That's where solid-state inorganic electrolytes have come in: they are significantly safer, and a garnet-type (type of structure) ceramic Li7La3Zr2O12, better known as LLZO, is now widely regarded as a promising solid-state electrolyte material for its high ionic conductivity and compatibility with Li metal. However, producing high-density LLZO electrolytes requires very high sintering temperatures, as high as 1200 °C. This is both energy inefficient and time-consuming, making large-scale production of LLZO electrolytes difficult. In addition, the poor physical contact between brittle LLZO electrolytes and the electrode materials usually results in high interfacial resistance, greatly limiting their application in all-solid-state Li-metal batteries.
Thus, a team led by Professor Kiyoshi Kanamura at Tokyo Metropolitan University set out to develop a flexible composite LLZO sheet electrolyte which can be made at room temperature. They cast a LLZO ceramic slurry onto a thin polymer substrate, like spreading butter on toast. After drying in a vacuum oven, the 75-micron thick sheet electrolyte was soaked in an ionic liquid (IL) to improve its ionic conductivity. ILs are salts which are liquid at room temperature, known to be highly conductive while being almost non-flammable and non-volatile. Inside the sheets, the IL successfully filled the microscopic gaps in the structure and bridged the LLZO particles, forming an efficient pathway for Li-ions. They also effectively reduced interfacial resistance at the cathode. On further investigation, they found that Li-ions diffused through both the IL and the LLZO particles in the structure, highlighting the role played by both. The synthesis is simple and suitable for industrial production: the whole process is carried out at room temperature without any need for high-temperature sintering.
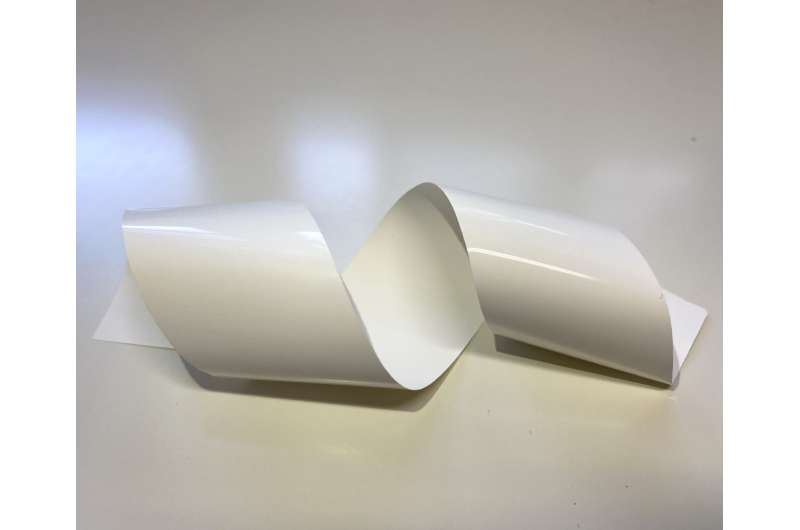

Though challenges remain, the team say that the mechanical robustness and operability of the flexible composite sheet at a wide range of temperatures makes it a promising electrolyte for Li-metal batteries. The simplicity of this new synthesis method may mean that we will see high capacity lithium metal batteries on the market sooner than we think.
More information: Eric Jianfeng Cheng et al, Ceramic-Based Flexible Sheet Electrolyte for Li Batteries, ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces (2020). DOI: 10.1021/acsami.9b21251
Journal information: ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces
Provided by Tokyo Metropolitan University