Scientists discover new way to reconstruct what extinct animals looked like
Scientists could be set to reveal the most accurate depictions of ancient vertebrates ever made after a world-first discovery at University College Cork (UCC) in Ireland.
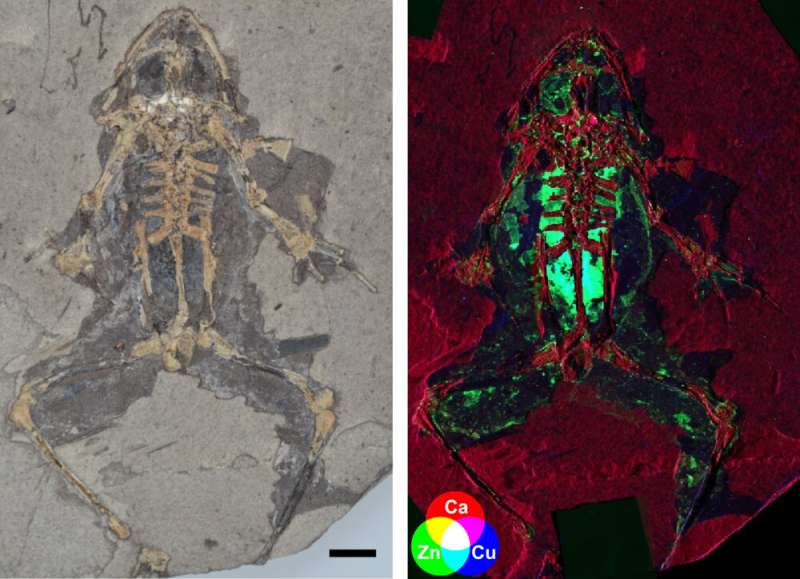
UCC palaeontologists have discovered a new way to reconstruct the anatomy of ancient vertebrate animals, analyzing the chemistry of fossilized melanosomes from internal organs.
The study, published today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, was led by UCC's Valentina Rossi and her supervisor Dr. Maria McNamara in collaboration with an international team of chemists from the US and Japan.
The team used cutting-edge synchrotron techniques to analyze the chemistry of the fossil and modern melanosomes using X-rays, allowing them to peer inside the anatomy of fossils and uncover hidden features.
Until recently, most studies on fossil melanin have focused on the skin and feathers, whereas here the pigment is linked to visible color. Unexpectedly, the new study also showed that melanin is abundant in internal organs of modern amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals, and their fossil counterparts.
"This discovery is remarkable in that it opens up a new avenue for reconstructing the anatomy of ancient animals. In some of our fossils we can identify skin, lungs, the liver, the gut, the heart, and even connective tissue," said senior author Dr. Maria McNamara.
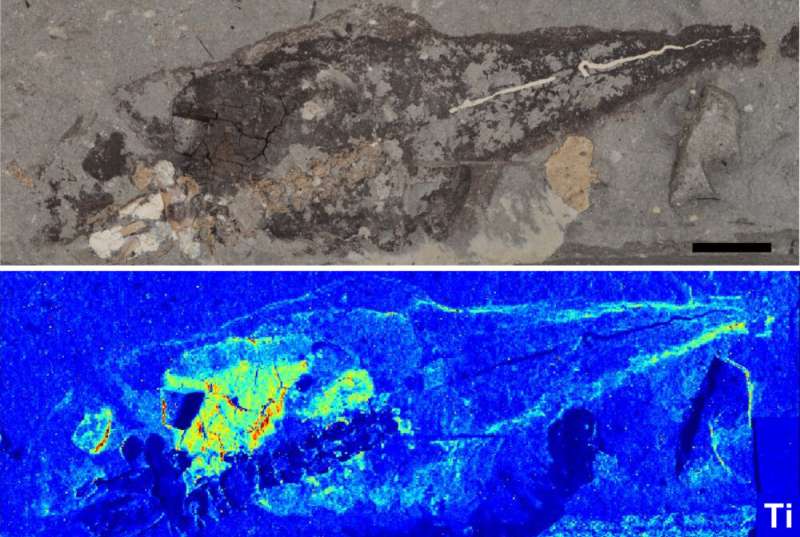

"What's more, this suggests that melanin had very ancient functions in regulating metal chemistry in the body going back tens, if not hundreds, of millions of years."
The team made the initial discovery of internal melanosomes last year on fossil frogs. "After the pilot study, we had a hunch that these features would turn out to be more widespread across vertebrates. But we never guessed that the chemistry would be different in different organs," Rossi said.
The advent of new synchrotron X-ray analysis techniques "allows us to harness the energy of really fast-moving electrons to detect minute quantities of different metals in the melanosomes."
The fossils are so well-preserved that even the melanin molecule can be detected.
More information: Valentina Rossi et al. Tissue-specific geometry and chemistry of modern and fossilized melanosomes reveal internal anatomy of extinct vertebrates, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2019). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1820285116
Journal information: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Provided by University College Cork



















