NASA gets an infrared view of Hurricane Oscar
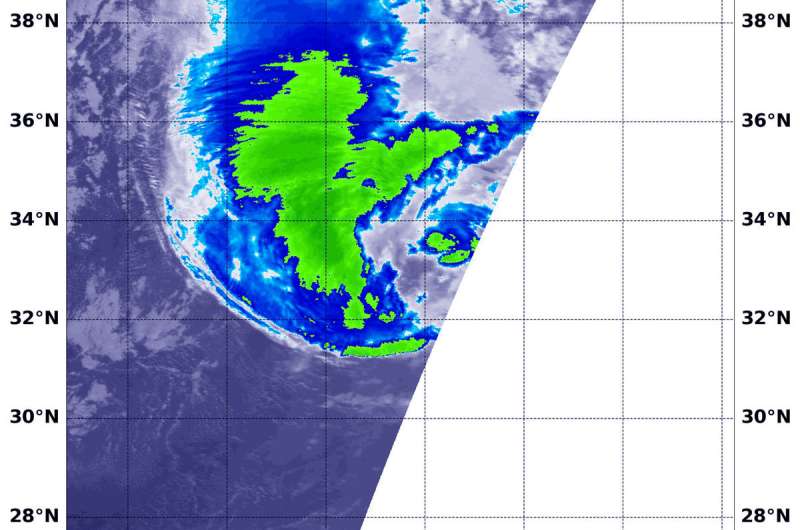
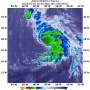
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the North Atlantic Ocean and gathered temperature data on Hurricane Oscar. The data showed the bulk of strong storms were in the northwestern quadrant as Oscar began transitioning into an extra-tropical storm.
On Oct. 31 at 2:15 a.m. EDT (0615 UTC) the MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite gathered infrared data on Oscar. Infrared data provides temperature information. Strongest thunderstorms were west and northwest of the center where MODIS found cloud top temperatures as cold as minus 63 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 53 Celsius). NASA research has shown that cloud tops with temperatures that cold were high in the troposphere and have the ability to generate heavy rain.
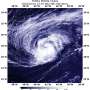
At 5 a.m. EDT (0900 UTC) on Oct. 31 the center of Hurricane Oscar was located near latitude 34.1 degrees north and longitude 53.6 degrees west. That's about 660 miles (1,060 km) east-northeast of Bermuda. Oscar is moving toward the northeast near 22 mph (35 kph). A faster north-northeast to northeast motion is expected during the next few days. Maximum sustained winds have decreased to near 75 mph (120 kph) with higher gusts. The estimated minimum central pressure is 982 millibars.
The National Hurricane Center noted at 11 a.m. EDT (1500 UTC), "Oscar is quickly transforming into an extratropical low. Although there is still a little bit of deep convection just north of the center, a more prominent cloud shield extends northward from the western part of the circulation."
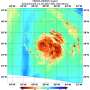
NOAA's GOES-16 satellite imagery showed Oscar's center nearly embedded within a frontal zone and cold air moving into the back side of the system.
Oscar is expected to become an extratropical low over the north-central Atlantic Ocean by tonight, Oct. 31 (EDT). Although gradual weakening is expected during the next several days, Oscar is expected to remain a powerful post-tropical cyclone over the north-central and northeastern Atlantic Ocean into the weekend.
Although far from land, large swells generated by Oscar will affect Bermuda through Wednesday, Oct. 31.
Provided by NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center