Emissions in savannas triple previous estimates
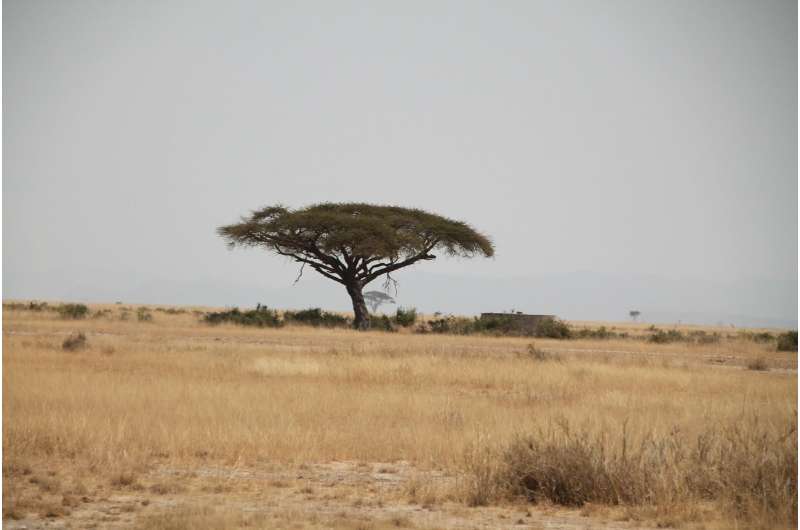

Widespread tree felling in African savannas is producing at least three times as many carbon emissions as was previously thought, research suggests.
The findings highlight the extent to which humans are impacting one of the world's major ecosystems – the Miombo woodlands, which cover 2.5 million square kilometres, across countries including Angola, Zambia, Tanzania and Mozambique.
At the same time, however, the growing number of trees in remote parts of these woodlands is helping to offset the emissions, researchers say.
Tree removal
The study is the first to provide an in-depth analysis of areas gaining carbon while also losing it through degradation – a process where some, but not all, trees are removed, usually as a result of logging and fire.
Until now, scientists had no way to measure these processes over such a large area.
Degradation is particularly difficult to detect using satellite imaging as vegetation can often appear unchanged.
Carbon losses
Edinburgh researchers used radar satellite data to show that degradation releases around twice as much carbon as deforestation – the clearing of entire areas for commercial activities. These losses are widespread close to major cities and roads.
Combined carbon losses from degradation and deforestation are between three and six times higher than previously thought, depending on the data used, the team says.
The main cause of degradation is to provide fuel for cooking and heating, mostly in the form of charcoal. Woodlands provide nearly 80 per cent of the energy used in the region, and the practice is often unregulated, leading to extensive overharvesting, researchers say.
"We knew that degradation was a problem, but this new approach means it is now much easier and cheaper for countries to monitor their natural resources and to target actions on the ground to mitigate these losses," says Dr. Casey Ryan.
Woodland regrowth
The previously unmeasured increases in carbon may be happening as more people move closer to cities, the team says.
It could also be linked to reductions in the number of elephants, and increased plant growth rates caused by rising carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere.
The study is published in the journal Nature Communications.
"While the rates of carbon loss we found are alarming, there is some cause for optimism. It is clear that in areas far from human influence, trees are taking in more carbon from the atmosphere. If more land is protected or used in a sustainable way, woodlands can recover relatively quickly," says Dr. Iain McNicol
Journal information: Nature Communications
Provided by University of Edinburgh