New technique lets doctors predict disease severity
An international team of researchers has found a way to diagnose disease and predict patient outcomes simply by measuring unbelievably small changes in interactions between molecules inside the body. The simple new technique could offer vastly superior predictions of disease severity in a huge range of conditions with a genetic component, such as Alzheimer's, autism, cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, schizophrenia and depression.
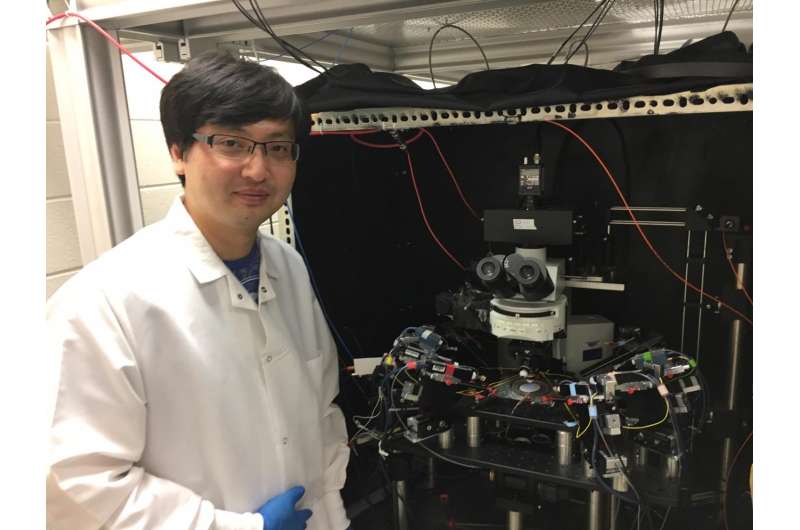
Gene mutations that cause disease physically alter the interactions of molecules that cells use to communicate with each other. Until now, scientists have had no easy way to measure the incredibly subtle changes in these interaction forces. But researcher J. Julius Zhu, PhD, of the University of Virginia School of Medicine, and his collaborators have developed a method to accurately and efficiently calculate these tiny changes. It's a feat that requires incredible precision: Force is typically measured in newtons - the amount of force needed to accelerate one kilogram of mass one meter per second squared - but Zhu's technique measures on a scale of piconewtons - one trillionth of a newton.
Zhu, of UVA's Department of Pharmacology, and his colleagues have used the new technique to show that gene mutations responsible for mental-health diseases change molecular interactions by a few piconewtons. These small changes then have a tremendous ripple effect. The researchers found the molecular changes lead to harmful changes in how the cells communicate - and, ultimately, in cognitive ability. By measuring the molecular changes, the scientists could predict the resulting cognitive impairment. In essence, the researchers are directly linking these tiny molecular changes to big changes in human behavior.
Zhu's approach represents a new use for a high-tech scientific instrument called "optical tweezers" that uses a highly focused laser to hold and move microscopic objects, much like regular tweezers might be used to grip and move a splinter. Using the optical tweezers, the scientists can measure the force required to break up intermolecular bonds between the signaling molecules inside the body, allowing them gauge the effects of gene mutations in patients. The researchers say the technique is simple to do and will dramatically improve our ability to diagnose mental illness and many other diseases.
The researchers have described their work in an article published online by the scientific journal Small.
More information: Chae-Seok Lim et al, Piconewton-Scale Analysis of Ras-BRaf Signal Transduction with Single-Molecule Force Spectroscopy, Small (2017). DOI: 10.1002/smll.201701972
Journal information: Small
Provided by University of Virginia