Programmed proteins might help prevent malaria
Despite decades of malaria research, the disease still afflicts hundreds of millions and kills around half a million people each year - most of them children in tropical regions. Part of the problem is that the malaria parasite is a shape-shifter, making it hard to target. But another part of the problem is that even the parasite's proteins that could be used as vaccines are unstable at tropical temperatures and require complicated, expensive cellular systems to produce them in large quantities. Unfortunately, the vaccines are most needed in areas where refrigeration is lacking and funds to buy vaccines are scarce. A new approach developed at the Weizmann Institute of Science, recently reported in Proceedings of the National Academy of Science (PNAS), could, in the future, lead to an inexpensive malaria vaccine that can be stored at room temperature.
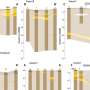
The RH5 protein is one of the malaria parasite's proteins that have been tested for use as a vaccine. This protein is used by the parasite to anchor itself to the red blood cells it infects. Using the protein as a vaccine alerts the immune system to the threat without causing disease, thus enabling it to mount a rapid response when the disease strikes, and to disrupt the parasite's cycle of infection. Research student Adi Goldenzweig and Dr. Sarel Fleishman of the Institute's Biomolecular Sciences Department decided to use the computer-based protein design tools they have been developing in Fleishman's lab to improve the usefulness of this protein.
Based on software they have been creating for stabilizing protein structures, Goldenzweig developed a new program for "programming" proteins used in vaccines against infectious diseases. Such proteins, because they are under constant attack by the immune system, tend to mutate from generation to generation. So the program she developed uses all the known information on different configurations of the protein sequence in different versions of the parasite. "The parasite deceives the immune system by mutating its surface proteins. Paradoxically, the better the parasite is at evading the immune system, the more clues it leaves for us to use in designing a successful artificial protein," she says.
The researchers sent the programmed artificial protein to a group in Oxford that specializes in developing a malaria vaccine. This group, led by Prof. Matthew Higgins and Simon Draper, soon had good news: The results showed that, in contrast with the natural ones, the programmed protein can be produced in simple, inexpensive cell cultures, and in large quantities. This could significantly lower production costs. In addition, it is stable at temperatures of up to 50o C, so it won't need refrigeration. Best of all, in animal trials, the proteins provoked a protective immune response. "The method Adi developed is really general," says Fleishman. "It has succeeded where others have failed, and because it is so easy to use, it might be applied to emerging infectious diseases like Zika or Ebola, when quick action can stop an epidemic from developing."
Fleishman and his group are currently using their method to test a different strategy for treating malaria, based on targeting the RH5 protein itself and blocking its ability to mediate the contact between the parasite and human red blood cells.
More information: Ivan Campeotto et al. One-step design of a stable variant of the malaria invasion protein RH5 for use as a vaccine immunogen, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2017). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1616903114
Journal information: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Provided by Weizmann Institute of Science