Device to start heavy equipment at temperatures as cold as −60 C

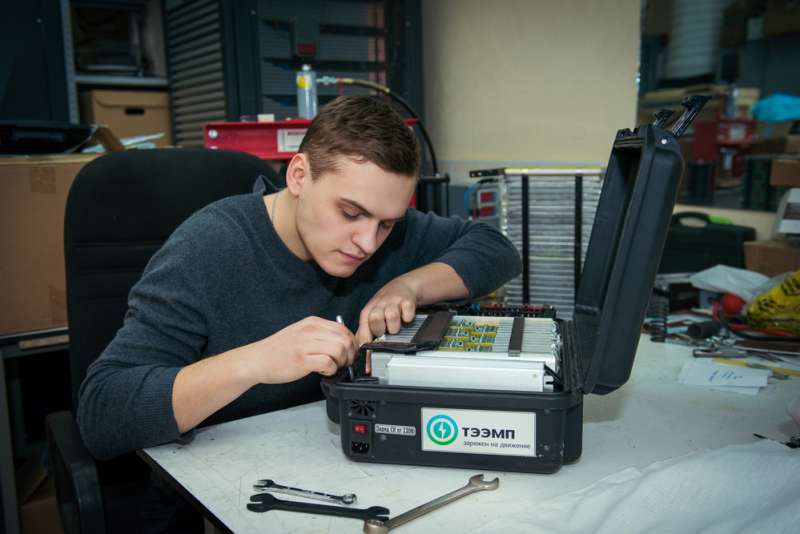
Together with TEEMP (a company in the RENOVA group), a group of NUST MISIS scientists led by Professor Mikhail Astakhov, head of the NUST MISIS Department of Physical Chemistry, has completed the testing of an innovative starter system based on supercapacitors. The autonomous system is able to start the engines of heavy-wheeled trucks, tractors, other Caterpillar equipment, and aviation equipment at extremely low temperatures (up to -60 °C).
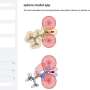
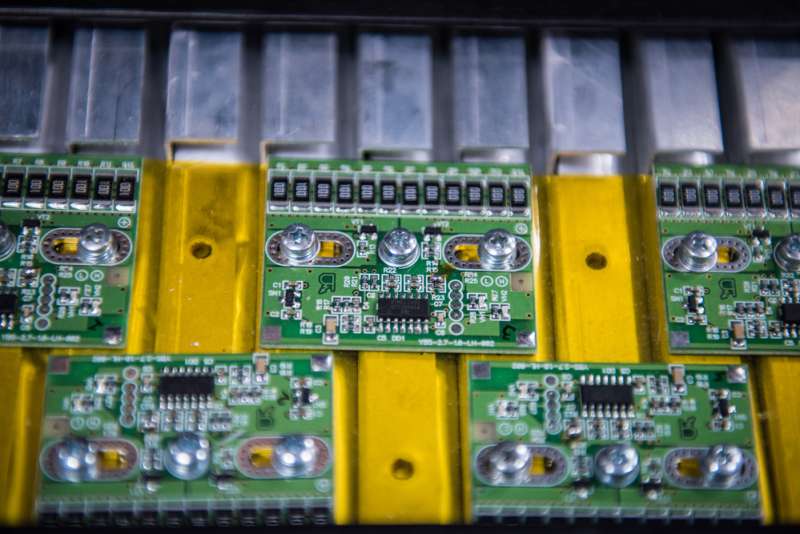
The self-contained unit, which was designed to run aircraft and on-board equipment, engine vessels of small aircraft, and heavy machinery at low temperatures, is a "coffer" containing a hybrid electric energy storage device based on a supercapacitor module and gasoline generator. In this configuration, the generator recharges the supercapacitor, which simultaneously produces a very powerful launcher charge.
The main element of the supercapacitor—the electricity storage—is the nanocarbon material obtained by NUST MISIS's research team. The nanocarbon material has a uniquely developed surface structure that holds the maximum surface area per unit volume, due to what are called "whiskers."
According to Vladimir Tumanov, the head of the project from the TEEMP side, "Our team has proposed a fundamentally new ideology of the design and technology used for the assembly of supercapacitor modules, and because of this innovation, the complexity of manufacturing storage has been considerably reduced. At the same time, equally original technology for manufacturing electrode materials from organic fibers was suggested by the NUST MISIS Department of Physical Chemistry, which is led by Mikhail Astakhov. Together, these two ideas will allow us to reduce the production cost of the energy storage unit by almost three times."
The new technology provides more efficient storage and energy accumulation through braking for hybrid and electric vehicles. This material can be used in stationary energy, pulse engineering, and even in medicine—for things like cardiac pacemakers, CT scanners, and X-ray machines.
The starter system device works in a standalone mode, as it doesn't require the presence of a main power outlet, and at fully-charged conditions, it is able to start a dump truck 10 times in a row and at temperatures ranging from -40 °C to -60° C, among other things. Additionally, the starter system can be used to launch light aircraft for general-purpose aviation, which requires a large amount of power in a short period of time, something too demanding for regular batteries.

"The new technology, developed at the NUST MISIS Department of Physical Chemistry and under the supervision of Professor Mikhail Astakhov, has massive application opportunities in various industries—environmentally friendly transportation, the construction of lifting machines, an uninterruptible power system and quality control of energy, and even pulse and medical technologies," said Alevtina Chernikova, Rector of NUST MISIS.
In comparison with current analogues, the module based on TEEMP`s supercapacitors has improved operating characteristics, namely its specific electric potential and energy capacity. Compared with existing devices, this unique construction allows the field of engineering to reduce module weight and size by 30 percent.
TEEMP Company is planning to open the first industrial production of these innovative supercapacitors in Khimki, a city in the Moscow oblast, in the first quarter of 2017.