Researchers watch biomolecules at work
Scientists at the University of Bonn have succeeded in observing an important cell protein at work using a method that measures structural changes within complex molecules. The procedure makes it possible to elucidate such processes in the natural environment. The researchers are also providing a tool kit, which allows a wide range of molecules to be measured. Their study has been published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
To open a Christmas season walnut, we usually use a nutcracker. The simplest of them consists of two arms that move against each other around a joint and can thus exert pressure on the shell.
Cellular molecules also alter their spatial structure as they work – similar to the nutcracker, which has arms that open or close. These conformational changes tell experts a great deal about the way in which the molecule fulfills its job. Unfortunately, it is very difficult to measure these kind of movements because they occur on a very small length scale. This complicates the observation of structural changes in the natural cellular environment, where countless simultaneous processes make it very hard to isolate any specific information from the general noise.
The working group from the Institute for Physical and Theoretical Chemistry at the University of Bonn has now succeeded in doing this. To this end, the scientists further developed a method that has been used for many years to measure distances within large molecules. "However, this normally only works in a test tube," explains the head of the study, Prof. Olav Schiemann. "In contrast, our technique can also be used in cells."
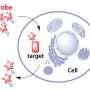
The researchers used what is known as electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy (EPR) for their measurements. The molecule to be measured is usually given a magnetic marker at two different sites. Through radiation with microwaves, the polarity of one of these mini magnets is reversed. The magnetic field emitted by it is thus changed, which in turn influences the second mini magnet. This influence is greater the closer both markers are to each other.
"We now measure how strongly the second magnet reacts to the reverse polarity of the first," explains Schiemann. "From this, we can ascertain the distance between both markers." If – metaphorically speaking – both arms of the nutcracker are marked in this way, their movement against each other can be understood.
Magnetic ruler measurements
In principle, the technique is not new. "However, we have succeeded in producing a new kind of label with which we can mark a wide range of biomolecules in a site-specific way", explains Schiemann's staff member Jean Jacques Jassoy. Usually, these labels consist of radicals – which are chemical compounds that carry a single free electron. The electron acts as a magnet during the measurement. The problem here: single electrons are highly reactive – they try to form pairs of electrons as quickly as possible. The chemists at the University of Bonn thus used a very stable radical in their work – a so called trityl group. They created various derivatives of this trityl radical. Each of these magnetic markers is designed to target specific sites within biomolecules and thus enables several approaches for the structural analysis of different biomolecules.
In their study, the researchers used this methodological advance to investigate a protein from the cytochrome P450 group. These proteins occur in almost all living beings and fulfill important tasks, for instance during oxidation processes in the cell. "With our method, we were able to precisely measure the distance between two areas of the cytochrome to a fraction of a millionth of a millimeter," emphasizes Schiemann´s staff member Andreas Berndhäuser.
The procedure is suitable for making biomolecule conformational changes visible in the cell. At the same time, it also generally facilitates the clarification of molecular structures. Schiemann: "We are thus providing researchers with a new tool kit that could help answer many biochemical questions."
More information: J. Jacques Jassoy et al. Versatile Trityl Spin Labels for Nanometer Distance Measurements on Biomolecules In Vitro and within Cells, Angewandte Chemie International Edition (2016). DOI: 10.1002/anie.201609085
Journal information: Angewandte Chemie International Edition
Provided by University of Bonn