Discovering a new force driving cell contraction during development and organogenesis
CRG scientists describe a new mechanism shaping cells and generating cell contractile forces during development and organogenesis. The new mechanism, which has been published today in the journal Developmental Cell, includes strategies shared with programmed cell death but which have not previously been directly associated with force generation. Studying developmental processes contributes to a better understanding of organ development and maintenance. Also, the specific process of dorsal closure described in this work is one of the most studied ones because of its similarity with wound healing.
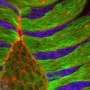
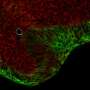
Cells and tissues must generate forces to shape organs and for proper development. A team of scientists led by Jérôme Solon at the Centre for Genomic Regulation has just described a new mechanism for the generation of the forces that drive cell movements during development. They were particularly focused on one of the most studied developmental processes: the Drosophila dorsal closure.
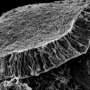
Dorsal closure is a process by which skin cells on the embryo stretch over a gap to close it. Briefly, accepted mechanism of this process has been that the edges of the gap form a kind of zipper that pulls the skin cells of the embryo together, to shape them and to lead to the next development stage. There are many research groups studying development and some of them focus in particular on dorsal closure because it is genetically and mechanically similar to wound healing in mammals such as ourselves.
"Mechanisms shaping cells and tissues described until now are based on forces generated by the remodelling of the cell cytoskeletal meshwork and structures that pull, push or shrink cells. What we have now described is that cells can also generate forces simply by modulating their volume", says Jérôme Solon, group leader of the Biomechanics of Morphogenesis group at the CRG in Barcelona.
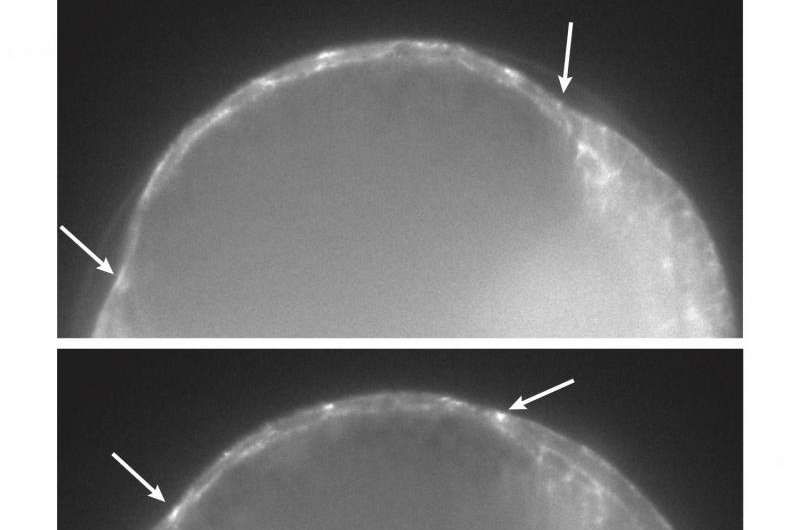
Solon and colleagues made a quantitative description of dorsal closure at a tri-dimensional level. They imaged the cells and, together with the physicist Guillaume Salbreux at the Francis Crick Institute in London, built a 3D model to enhance our understanding of what was happening at the single cell level. "Surprisingly, we found that cells were not elongating or changing their shape in the manner that was previously thought, but that the cells were actually changing their volume and shrinking." When looking at the cells in most of the mechanisms underlying tissue contraction during development, we can see how they are changing their shape, turning flat cells into pear-like cells without an alteration in volume. However, in this case, the researchers observed that cells retain their thickness but decreased their volume, getting smaller.
When cell death is the engine for life
"The most curious thing is that the mechanisms driving these volume changes are the same as those that have been found during programmed cell death or apoptosis. So, it is important for us to highlight the dual role of apoptosis in this particular developmental process. We feel that these mechanisms are likely to play important roles in other morphogenetic processes shaping tissues and organs, such as wound healing and limb or brain development", concludes Solon.
More information: Saias et al. Decrease in Cell Volume Generates Contractile Forces Driving Dorsal Closure, Developmental Cell (2015). dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2015.03.013
Journal information: Developmental Cell
Provided by Center for Genomic Regulation