Verifying that sorghum is a new safe grain for people with celiac disease

Strong new biochemical evidence exists showing that the cereal grain sorghum is a safe food for people with celiac disease, who must avoid wheat and certain other grains, scientists are reporting. Their study, which includes molecular evidence that sorghum lacks the proteins toxic to people with celiac disease, appears in ACS' Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry.
Paola Pontieri and colleagues explain that those gluten proteins, present in wheat and barley, trigger an immune reaction in people with celiac disease that can cause abdominal pain and discomfort, constipation, diarrhea and other symptoms. The only treatment is lifelong avoidance of gluten. Sorghum, they note, has emerged as an alternative grain for people with celiac disease. In Western countries, sorghum traditionally has been an animal feed. But in Africa and India, it long has been a food for people. Recently, U.S. farmers have begun producing sorghum hybrids that are a white grain, known as "food-grade" sorghum. The researchers set out to make a detailed molecular determination of whether sorghum contains those toxic gluten proteins.
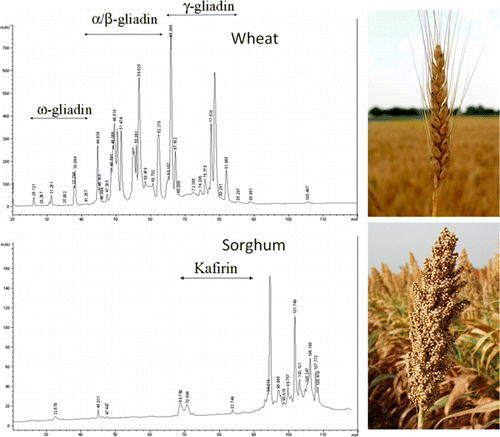
They describe evidence from an analysis of the recently published sorghum genome, the complete set of genes in the plant, and other sources, that verify the absence of gluten proteins. The authors also report that sorghum has high nutritional value. "Food-grade sorghums should be considered as an important option for all people, especially celiac patients," the report concluded.
More information: Sorghum, a Healthy and Gluten-free Food for Celiac Patients As Demonstrated by Genome, Biochemical, and Immunochemical Analyses, J. Agric. Food Chem., 2013, 61 (10), pp 2565–2571 DOI: 10.1021/jf304882k
Abstract
Wheat (Triticum spp. L.), rye (Secale cereal L.), and barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) seeds contain peptides toxic to celiac patients. Maize (Zea mays L.) and rice (Oryza sativa L.) are distant relatives of wheat as well as sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) and are known to be safe for celiacs. Both immunochemical studies and in vitro and in vivo challenge of wheat-free sorghum food products support this conclusion, although molecular evidence is missing. The goal of the present study was to provide biochemical and genetic evidence that sorghum is safe for celiac patients. In silico analysis of the recently published sorghum genome predicts that sorghum does not contain peptides that are toxic for celiac patients. Aqueous/alcohol-soluble prolamins (kafirins) from different sorghum varieties, including pure lines and hybrids, were evaluated by SDS-PAGE and HPLC analyses as well as an established enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) based on the R5 antibody. These analyses provide molecular evidence for the absence of toxic gliadin-like peptides in sorghum, confirming that sorghum can be definitively considered safe for consumption by people with celiac disease.
Journal information: Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
Provided by American Chemical Society