Into the quantum internet at the speed of light
Not only do optical fibers transmit information every day around the world at the speed of light, but they can also be harnessed for the transport of quantum information. In the current issue of Nature Photonics, a research team of Innsbruck physicists led by Rainer Blatt and Tracy Northup report how they have directly transferred the quantum information stored in an atom onto a particle of light. Such information could then be sent over optical fiber to a distant atom.
Thanks to the strange laws of quantum mechanics, quantum computers would be able to carry out certain computational tasks much faster than conventional computers. Among the most promising technologies for the construction of a quantum computer are systems of single atoms, confined in so-called ion traps and manipulated with lasers. In the laboratory, these systems have already been used to test key building blocks of a future quantum computer. "Currently, we can carry out successful quantum computations with atoms," explain Andreas Stute and Bernardo Casabone, both PhD students at the University of Innsbruck's Institute for Experimental Physics. "But we are still missing viable interfaces with which quantum information can be transferred over optical channels from one computer to another."
What makes the construction of these interfaces especially challenging is that the laws of quantum mechanics don't allow quantum information to be simply copied. Instead, a future quantum internet – that is, a network of quantum computers linked by optical channels – would have to transfer quantum information onto individual particles of light, known as photons. These photons would then be transported over an optical-fiber link to a distant computing site. Now, for the first time, quantum information has been directly transferred from an atom in an ion trap onto a single photon. The work is reported in the current issue of Nature Photonics by a research team led by Tracy Northup and Rainer Blatt.
Quantum networkers
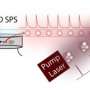
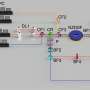
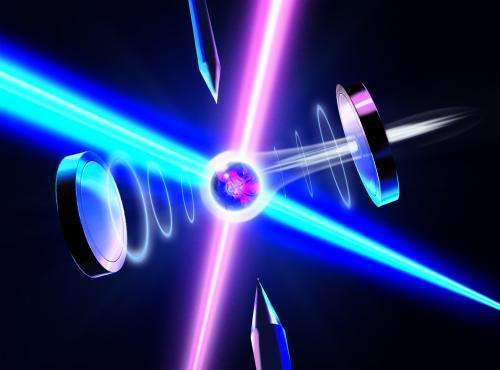
The University of Innsbruck physicists first trap a single calcium ion in an ion trap and position it between two highly reflective mirrors. "We use a laser to write the desired quantum information onto the electronic states of the atom," explains Stute. "The atom is then excited with a second laser, and as a result, it emits a photon. At this moment, we write the atom's quantum information onto the polarization state of the photon, thus mapping it onto the light particle." The photon is stored between the mirrors until it eventually flies out through one mirror, which is less reflective than the other. "The two mirrors steer the photon in a specific direction, effectively guiding it into an optical fiber," says Casabone. The quantum information stored in the photon could thus be conveyed over the optical fiber to a distant quantum computer, where the same technique could be applied in reverse to write it back onto an atom.
More information: Stute, A. et al. Quantum-state transfer from an ion to a photon. Nature Photonics 2013. DOI: 10.1038/NPHOTON.2012.358
Journal information: Nature Photonics
Provided by University of Innsbruck