New 3D printing process could lead to DIY drugstores

(Phys.org) -- A new 3D printing process developed at the University of Glasgow could revolutionise the way scientists, doctors and even the general public create chemical products.
Professor Lee Cronin, Gardiner Chair of Chemistry at the University, believes his research could lead to the development of home chemical fabricators which consumers could use to design and create medicine at home.
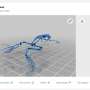
A new research paper, published in the journal Nature Chemistry today, outlines how the process has been proven to work. Using a commercially-available 3D printer operated by open-source computer-aided design software, Professor Cronin and his team have built what they call ‘reactionware’, special vessels for chemical reactions which are made from a polymer gel which sets at room temperature.
By adding other chemicals to the gel deposited by the printer, the team have been able to make the vessel itself part of the reaction process. While this is common in large-scale chemical engineering, the development of reactionware makes it possible for the first time for custom vessels to be fabricated on a laboratory scale.
Professor Cronin said: “It’s long been possible to have lab materials custom-made to include windows or electrodes, for example, but it’s been expensive and time-consuming. We can fabricate these reactionware vessels using a 3D printer in a relatively short time. Even the most complicated vessels we’ve built have only take a few hours.
“By making the vessel itself part of the reaction process, the distinction between the reactor and the reaction becomes very hazy. It’s a new way for chemists to think, and it gives us very specific control over reactions because we can continually refine the design of our vessels as required.
“For example, our initial reactionware designs allowed us to synthesize three previously unreported compounds and dictate the outcome of a fourth reaction solely by altering the chemical composition of the reactor.”
Although the technology they are developing is still at an early stage, the team, comprised of researchers from the University’s School of Chemistry and School of Physics and Astronomy, is also considering the long-term implications of developments in 3D printing technology.
Professor Cronin added: “3D printers are becoming increasingly common and affordable. It’s entirely possible that, in the future, we could see chemical engineering technology which is prohibitively expensive today filter down to laboratories and small commercial enterprises.
“Even more importantly, we could use 3D printers to revolutionise access to healthcare in the developing world, allowing diagnosis and treatment to happen in a much more efficient and economical way than is possible now.
“We could even see 3D printers reach into homes and become fabricators of domestic items, including medications. Perhaps with the introduction of carefully-controlled software ‘apps’, similar to the ones available from Apple, we could see consumers have access to a personal drug designer they could use at home to create the medication they need.”
Professor Cronin’s paper, titled ‘Integrated 3D-printed reactionware for chemical synthesis and analysis’, is published today in Nature Chemistry.
More information: Integrated 3D-printed reactionware for chemical synthesis and analysis, Nature Chemistry (2012) doi:10.1038/nchem.1313
Abstract
Three-dimensional (3D) printing has the potential to transform science and technology by creating bespoke, low-cost appliances that previously required dedicated facilities to make. An attractive, but unexplored, application is to use a 3D printer to initiate chemical reactions by printing the reagents directly into a 3D reactionware matrix, and so put reactionware design, construction and operation under digital control. Here, using a low-cost 3D printer and open-source design software we produced reactionware for organic and inorganic synthesis, which included printed-in catalysts and other architectures with printed-in components for electrochemical and spectroscopic analysis. This enabled reactions to be monitored in situ so that different reactionware architectures could be screened for their efficacy for a given process, with a digital feedback mechanism for device optimization. Furthermore, solely by modifying reactionware architecture, reaction outcomes can be altered. Taken together, this approach constitutes a relatively cheap, automated and reconfigurable chemical discovery platform that makes techniques from chemical engineering accessible to typical synthetic laboratories
Journal information: Nature Chemistry
Provided by University of Glasgow