Last update:
Nanophysics news

Space-based experiments could help to advance early cancer detection through blood tests
Imagine a sensor so sensitive it can detect early cancer in a single drop of blood, enabling diagnosis and treatment before the first symptoms—possibly before a tumor even forms.
Bio & Medicine
Sep 5, 2024
0
13

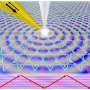
New method captures the stochastic dynamics in coherent X-ray imaging at the nanoscale
Coherent X-ray imaging has emerged as a powerful tool for studying both nanoscale structures and dynamics in condensed matter and biological systems. The nanometric resolution together with chemical sensitivity and spectral ...
Nanophysics
Sep 4, 2024
0
3

Metasurfaces: Tiny tech with big potential
Imagine manipulating light with ultra-thin, flat sheets instead of bulky lenses and mirrors. That's the promise of metasurfaces, a nanostructure technology that can twist and bend light in ways never before possible.
Nanophysics
Sep 4, 2024
0
1

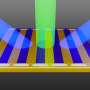
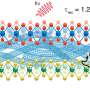
Nanostructures enable on-chip lightwave-electronic frequency mixer
Imagine how a phone call works: Your voice is converted into electronic signals, shifted up to higher frequencies, transmitted over long distances, and then shifted back down so it can be heard clearly on the other end. The ...
Nanophysics
Sep 4, 2024
0
109

Low-energy ion implantation enables 2D lateral p-n junction construction
The feature size of silicon-based transistors is approaching the theoretical limit, which puts forward higher requirements for the atomic level manufacturing of semiconductors. The basic idea of atomic level manufacturing ...
Nanophysics
Sep 2, 2024
0
1

Advances in optical micronanofiber-enabled tactile sensors and soft actuators
A perfect combination of fiber optics and micro/nanotechnology, optical micro/nanofiber (MNF) is a new type of micro/nano-waveguide structure developed in recent years.
Nanophysics
Aug 30, 2024
0
0

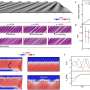
Spin-controlled generation of a complete polarization set with randomly interleaved plasmonic metasurfaces
Optical metasurfaces are finely crafted two-dimensional artificial nanostructures composed of meticulously designed arrays of ultrathin artificial atoms. These surfaces possess capabilities beyond natural materials, enabling ...
Nanophysics
Aug 30, 2024
0
1

Illuminating the unavoidable imperfections of nanostructures
A new study by a collaborative team from the University of Twente and the e-Science Center in Amsterdam compares the transmission of light through a utopian model with a real 3D nanostructure. These nanostructures are integral ...
Nanophysics
Aug 29, 2024
0
1

Manipulation of nanolight provides new insight for quantum computing and thermal management
A recent study led by University of Minnesota Twin Cities researchers provides fundamental insight into how light, electrons, and crystal vibrations interact in materials. The research has implications for developing on-chip ...
Nanophysics
Aug 26, 2024
0
42

New varactor enhances quantum dot device measurements at millikelvin temperatures
The development of quantum computing systems relies on the ability to rapidly and precisely measure these systems' electrical properties, such as their underlying charge and spin states. These measurements are typically collected ...

Researchers demonstrate metasurfaces that control thermal radiation in unprecedented ways
Researchers with the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) have experimentally demonstrated that metasurfaces (two-dimensional materials structured at the nanoscale) can precisely control ...
Nanophysics
Aug 23, 2024
0
80

Low-cost flexible metasurfaces to increase the efficiency of optoelectronic devices
Metasurfaces are two-dimensional counterparts of metamaterials, which are artificial materials that possess unusual characteristics. With a variety of fascinatingly innovative and diverse uses, these specially-prepared surfaces ...
Nanophysics
Aug 22, 2024
0
4

Advancing nanoscale imaging capabilities with dynamic nuclear polarization
Dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) has revolutionized the field of nanoscale nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), making it possible to study a wider range of materials, biomolecules and complex dynamic processes such as how ...
Nanophysics
Aug 22, 2024
0
23

A world first: Qubit coherence decay traced to thermal dissipation
Physicists from Aalto University in Finland, alongside an international team of collaborators, have theoretically and experimentally shown that superconducting qubit coherence loss can be directly measured as thermal dissipation ...
Nanophysics
Aug 22, 2024
0
46

World's first micromachine twists 2D materials at will
Just a few years ago, researchers discovered that changing the angle between two layers of graphene, an atom-thick sheet of carbon, also changed the material's electronic and optical properties. They then learned that a "twist" ...
Nanophysics
Aug 22, 2024
0
147

Unveiling the power of hot carriers in plasmonic nanostructures
A new scientific review explores the exciting potential of hot carriers, energetic electrons generated by light in plasmonic nanostructures. These tiny structures hold immense promise for future technologies due to their ...
Nanophysics
Aug 16, 2024
0
0

Team develops method for control over single-molecule photoswitching
Scientists from the Department of Physical Chemistry at the Fritz Haber Institute have made an innovative discovery in nanoscale optoelectronics. The study, published in the journal Nature Communications and titled "Atomic-Precision ...
Nanophysics
Aug 15, 2024
0
107

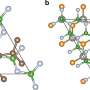
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions: Theoretical model could lead to switches and amplifiers
Researchers have developed a new theoretical modeling technique that could potentially be used in the development of switches or amplifiers in molecular electronics. The modeling technique is a collaboration between researchers ...
Nanophysics
Aug 15, 2024
0
138

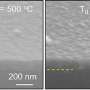
Photolithography research shows computer chips have the potential to become even smaller
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have been improving the resolution of a process known as photolithography. They hope to use their technique to help advance the miniaturization of computer chips.
Nanophysics
Aug 13, 2024
0
89

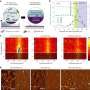
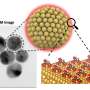
Carbon nanotubes study finds local solvation is decisive for fluorescence of biosensors
At Ruhr University, the groups of Professor Martina Havenith and Professor Sebastian Kruss collaborated for a new study, which took place as part of the Cluster of Excellence "Ruhr Explores Solvation," or RESOLV for short. ...
Nanophysics
Aug 12, 2024
0
0
Other news
How viruses move through insects for transmission of diseases

New dense sub-Saturn exoplanet discovered

Deserts' biggest threat? Flooding

Unprecedented spin properties revealed in new artificial materials

Managing aquatic plants: Why doing nothing is also an option

SpaceX launches all-civilian crew for first private spacewalk