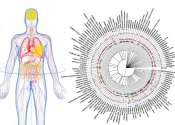
Advanced cell atlas opens new doors in biomedical research
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet have developed a web-based platform that offers an unprecedented view of the human body at the cellular level. The aim is to create an invaluable resource for researchers worldwide to ...