A faster sequence homology search algorithm based on database subsequence clustering
Sequence homology searches are widely used in genome studies. New DNA sequencers produce large amounts of sequence data, which require continual increases in the size of sequence databases.
As a result, homology searches require huge amounts of computational time, especially for metagenomic analysis. In metagenomic analysis, environmental samples (from soil, the sea, the human body, and so on) frequently include DNA sequences from many different species, and the reference database often does not contain closely-related genome sequences. This means that more sensitive approaches are required to identify novel genes. Even general homology search analyses using BLASTX become difficult in terms of computational cost.
Now, Yutaka Akiyama and colleagues at Tokyo Institute of Technology have developed a faster homology search method based on database subsequence clustering, and implemented it as GHOSTZ. The source code is freely available for download.
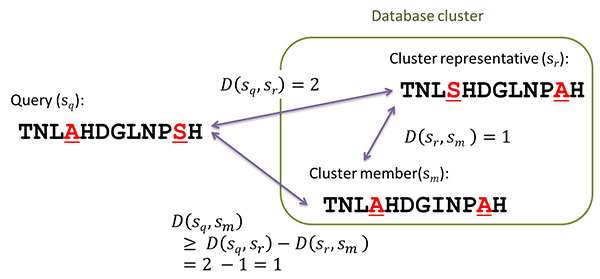
This method clusters similar subsequences from a database to perform an efficient seed search and ungapped extension by reducing alignment candidates based on triangle inequality.
When measured with metagenomic data, GHOSTZ is ~2.2-2.8 times faster than RAPSearch and is ~185-261 times faster than BLASTX.
The algorithm was designed for functional and taxonomic annotation in metagenome analysis, but it could also prove to be a useful tool in proteome research.
Publication details
"Faster sequence homology searches by clustering subsequences." Bioinformatics. 2015 Apr 15;31(8):1183-90. DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu780
Journal information: Bioinformatics
Provided by Tokyo Institute of Technology