The effect of molecular oxygen electron spin on the surface oxidation reaction
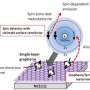
Mitsunori Kurahashi, a Chief Researcher of the Nano Characterization Unit, National Institute for Materials Science and Yasushi Yamauchi, a Group Leader in the same unit, presented the first spin-controlled O2 adsorption experiment indicating that the rate of surface oxidation is strongly affected by the electron spin of O2.
O2 adsorption on material surfaces is important as the initial step of catalytic reaction, corrosion and oxide film formation. O2 is magnetic due to its electron spin derived from two unpaired electrons. The potential effect of the O2 spin on the adsorption process has been pointed out theoretically, but the effect has been unclear because there has been no experimental evidence for it.
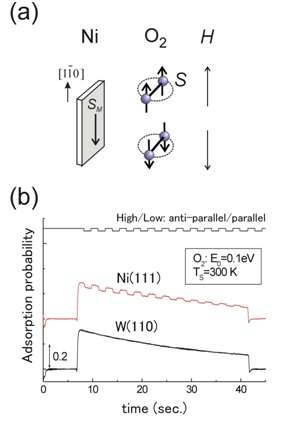
Kurahashi and Yamauchi have realized the spin- and alignment-resolved O2 adsorption experiment by combining the quantum-state-selected O2 beam, which has been originally developed by them, with a magnetized Ni film. Their experiment has shown that O2 adsorption probability depends on the orientation of the O2 spin relative to the magnetization of the Ni film. The spin dependency is significant especially at low kinetic energy conditions, and amounts to more than 40% at thermal energy. These results indicate that thermal oxidation rate of ferromagnetic materials such as iron and nickel depends strongly on the spin orientation between O2 and the surface. It has been concluded that the magnetic exchange interaction between O2 and the surface is the main cause of the observed spin dependency. It is well known that solid and/or liquid oxygen exhibit magnetism, but this research presented the first experimental evidence that the magnetic property of O2 has a strong influence on its chemical reactivity.
This research has established a new methodology for analyzing the spin effect in O2-surface interactions. Also, the observed clear spin effect may provide a firm basis to advance the theoretical technique for simulating oxygen adsorption.
More information: "Spin Correlation in O2 Chemisorption on Ni(111)." Phys. Rev. Lett. dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.114.016101
Journal information: Physical Review Letters
Provided by National Institute for Materials Science