New analysis eliminates a potential speed bump in quantum computing
A quantum particle can search for an item in an unsorted "database" by jumping from one item to another in superposition, and it does so faster than a classical computer ever could.
This assertion assumes, however, that the particle can directly hop from any item to any other. Any restriction on which items the particle can directly hop to could slow down the search.
"Intuition says that a symmetric database allows the particle to hop freely enough to retain the quantum speedup, but our research has shown this intuition to be false," says Tom Wong, a physicist at the University of California, San Diego.
In a paper accepted for publication by Physical Review Letters, the researchers used a technique familiar to physicists called "degenerate perturbation theory" in a novel way to prove that global symmetry is not required for a sped up search.
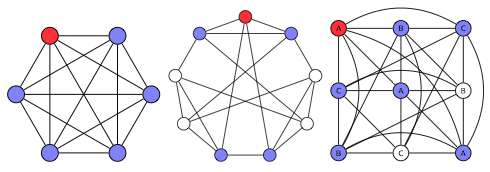
Information scientists represent the database to be searched as a graph. In globally symmetric graphs, the nodes can be swapped with each other such that the connections between them are preserved. "Strongly regular graphs" don't share this property, but this analysis shows they also support a fast search through local symmetries.
Their finding extends the use of this theory to the field of quantum information science and expands the kinds of data structures on which quantum computing outperforms classical computing.
Publication details
The paper is availabe now on the arXiv preprint server: arxiv.org/abs/1403.2228
Journal information: Physical Review Letters
Provided by University of California - San Diego