Wasp transcriptome creates a buzz
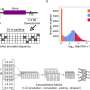
New research delivers a sting in the tail for queen wasps. Scientists have sequenced the active parts of the genome – or transcriptome – of primitively eusocial wasps to identify the part of the genome that makes you a queen or a worker. Their work, published in BioMed Central's open access journal Genome Biology, shows that workers have a more active transcriptome than queens. This suggests that in these simple societies, workers may be the 'jack-of-all-trades' in the colony - transcriptionally speaking - leaving the queen with a somewhat restricted repertoire.
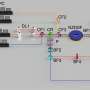
Studying primitively eusocial species - like these wasps - can tell us about how sociality evolves. Seirian Sumner and colleagues sequenced transcriptomes from the eusocial tropical paper wasps – Polistes canadensis. All social species ultimately evolved from a solitary ancestor – in this case a solitary wasp, who lays the eggs and feeds the brood. But how does this ancestral solitary phenotype split to produce specialised reproducers (queens) and brood carers (workers) when a species becomes social?
This paper gives a first insight into the secret lives of social insects. It shows that workers retain a highly active transcriptome, possibly expressing many of the ancestral genes that are required for our solitary wasp to be successful on her own. Conversely, queens appear to shut down a lot of their genes, presumably in order to be really good reproducers.
Long-standing analyses based on the fossil record holds ants and wasps in a clade known as Vespoidea, with bees as a sister group. The team reassess the relationships between the subfamilies of bees, wasps and ants and suggest that wasps are part of a separate clade from ants and bees, though further genome sequences and comparative data will help to resolve this controversy.
The dataset offers a first chance to analyse subfamily relationships across large numbers of genes, though further work is required before the term Vespoidia could be dropped, or reclassified. Sumner says: 'This finding would have important general implications for our understanding of eusociality as it would suggest that bees and ants shared an aculeate wasp-like ancestor, that ants are wingless wasps, and that bees are wasps that lost predacious behaviours.'
Their work suggests that novel genes play a much more important role in social behaviour than we previously thought.
More information: Transcriptome analyses of primitively eusocial wasps reveal novel insights into the evolution of sociality and the origin of alternative phenotypes, Pedro G Ferreira, Solenn Patalano, Ritika Chauhan, Richard Ffrench-Constant, Toni Gabaldon, Roderic Guigo and Seirian Sumner, Genome Biology (in press)
Journal information: Genome Biology
Provided by BioMed Central