Electrified graphene a shutter for light
(Phys.org) -- An applied electric voltage can prompt a centimeter-square slice of graphene to change and control the transmission of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths from the terahertz to the midinfrared.
The experiment at Rice University advances the science of manipulating particular wavelengths of light in ways that could be useful in advanced electronics and optoelectronic sensing devices.
In previous work, the Rice lab of physicist Junichiro Kono found a way to use arrays of carbon nanotubes as a near-perfect terahertz polarizer. This time, the team led by Kono is working on an even more basic level; the researchers are wiring a sheet of graphene – the one-atom-thick form of carbon – to apply an electric voltage and thus manipulate what’s known as Fermi energy. That, in turn, lets the graphene serve as a sieve or a shutter for light.
The discovery by Kono and his colleagues at Rice and the Institute of Laser Engineering at Osaka University was reported online this month in the American Chemical Society journal Nano Letters.
In graphene, “electrons move like photons, or light. It’s the fastest material for moving electrons at room temperature,” said Kono, a professor of electrical and computer engineering and of physics and astronomy. He noted many groups have investigated the exotic electrical properties of graphene at zero- or low frequencies.
“There have been theoretical predictions about the unusual terahertz and midinfrared properties of electrons in graphene in the literature, but almost nothing had been done in this range experimentally,” Kono said.
Key to the new work, he said, are the words “large area” and “gated.”
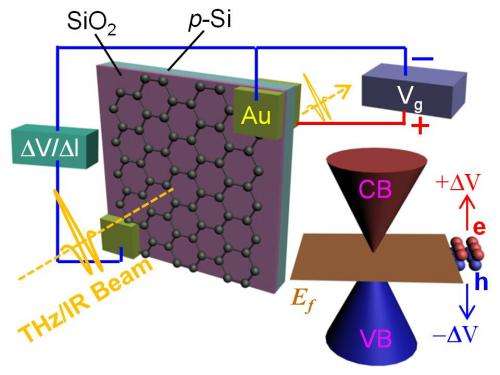
“Large because infrared and terahertz have long wavelengths and are difficult to focus on a small area,” Kono said. “Gated simply means we attached electrodes, and by applying a voltage between the electrodes and (silicon) substrate, we can tune the Fermi energy.”
Fermi energy is the energy of the highest occupied quantum state of electrons within a material. In other words, it defines a line that separates quantum states that are occupied by electrons from the empty states. “Depending on the value of the Fermi energy, graphene can be either p-type (positive) or n-type (negative),” he said.
Making fine measurements required what is considered in the nano world to be a very large sheet of graphene, even though it was a little smaller than a postage stamp. The square centimeter of atom-thick carbon was grown in the lab of Rice chemist James Tour, a co-author of the paper, and gold electrodes were attached to the corners.
Raising or lowering the applied voltage tuned the Fermi energy in the graphene sheet, which in turn changed the density of free carriers that are good absorbers of terahertz and infrared waves. This gave the graphene sheet the ability to either absorb some or all of the terahertz or infrared waves or let them pass. With a spectrometer, the team found that terahertz transmission peaked at near-zero Fermi energy, around plus-30 volts; with more or less voltage, the graphene became more opaque. For infrared, the effect was the opposite, he said, as absorption was large when the Fermi energy was near zero.
“This experiment is interesting because it lets us study the basic terahertz properties of free carriers with electrons (supplied by the gate voltage) or without,” Kono said. The research extended to analysis of the two methods by which graphene absorbs light: through interband (for infrared) and intraband (for terahertz) absorption. Kono and his team found that varying the wavelength of light containing both terahertz and infrared frequencies enabled a transition from the absorption of one to the other. “When we vary the photon energy, we can smoothly transition from the intraband terahertz regime into the interband-dominated infrared. This helps us understand the physics underlying the process,” he said.
They also found that thermal annealing – heating – of the graphene cleans it of impurities and alters its Fermi energy, he said.
Kono said his lab will begin building devices while investigating new ways to manipulate light, perhaps by combining graphene with plasmonic elements that would allow a finer degree of control.
Co-authors of the paper include former Rice graduate students Lei Ren, Jun Yao and Zhengzong Sun; Rice graduate student Qi Zhang; Rice postdoctoral researchers Zheng Yan and Sébastien Nanot; former Rice postdoctoral researcher Zhong Jin; and graduate student Ryosuke Kaneko, assistant professor Iwao Kawayama and Professor Masayoshi Tonouchi of the Laser Engineering Institute, Osaka University.
More information: pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/nl301496r
Journal information: Nano Letters
Provided by Rice University