Engineering next-generation smart separator membranes
A team of Korean researchers, affiliated with UNIST is receiving the media spotlight as they have proposed a green material strategy for the development of smart battery separators beyond the current state-of-the-art counterparts.
The findings appear in the July 6th issue of Nano Letters, co-authored by Prof. Sang-Young Lee (School of Energy and Chemical Engineering), Prof. Byeong-Su Kim (School of Natural Science), the lead authors of the study Jung-Hwan Kim (School of Energy and Chemical Engineering) and Minsu Gu (School of Energy and Chemical Engineering), and four others.
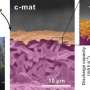
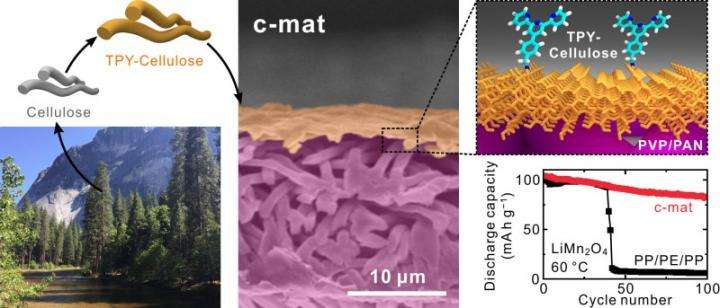
In the study, the research team presented a new class of battery seperator based on the hierarchical/asymmetric porous structure of the heterolayered nanomat ("c-mat separator"), as an unprecedented membrane opportunity to enable remarkable advances in cell performance far beyond those accessible with conventional battery separators.
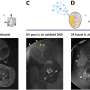
Among major battery components, separator membranes have not been the center of attention compared to other electrochemically active materials, despite their important roles in allowing ionic flow and preventing electrical contact between electrodes. This study introduces novel chemical functionalities to seperator membranes, thereby bringing unprecedented benefits to battery performance.
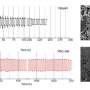
The c-mat separator consisted of a thin nanoporous TPY-CNF mat as the top layer and a thick macroporous electrospun PVP/PAN mat as the support layer. According to the research team, in addition to the aforementioned structural uniqueness, another salient feature of the c-mat separator is the higher ion conductivity compared with the existing PP/PE/PP separators.
"This ground-breaking discovery will pave the way towards next generation lithium-ion batteries, exhibiting significantly enhanced performance and increased energy efficiency," says JungHwan Kim, the lead author on the study.
The research team noted, "We envision that the c-mat separator, benefiting from its structural uniqueness and chemical functionalities, will open a new path for the development of high-performance smart separator membranes for potential use in next-generation power sources and in permselective membrane filtration systems for high mass flux/removal of heavy-metal ions."
More information: Jung-Hwan Kim et al, Functionalized Nanocellulose-Integrated Heterolayered Nanomats toward Smart Battery Separators, Nano Letters (2016). DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b02069
Journal information: Nano Letters