Experts demonstrate versatility of Sentinel-1
From climate change monitoring to supporting humanitarian aid and crisis situations, early data applications from the month-old Sentinel-1A satellite show how the radar mission's critical observations can be used to keep us and our planet safe.
Launched from Europe's Spaceport in French Guiana on 3 April, Sentinel-1A is the first satellite in Europe's Copernicus environmental monitoring network. The mission uses radar to provide an all-weather, day-and-night supply of imagery of Earth's surface.
At an event in Brussels today, experts who had been given access to early Sentinel-1A radar data presented how a variety of operational and scientific applications will benefit.
These [radar] images and their analyses will benefit European citizens, enterprises and decision makers, as well as the international scientific community. They will allow us to better protect our planet and improve the quality of life of our citizens," said Philippe Brunet, Director of Aerospace, Maritime, Security and Defence Industries at the European Commission.
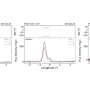
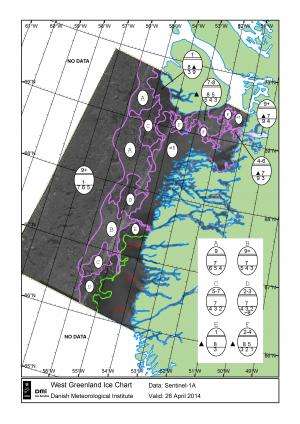
Leif Toudal Pedersen from the Danish Meteorological Institute and involved in the Copernicus marine core service MyOcean presented the first 'ice chart' from Sentinel-1A, showing how the radar will be used to map sea-ice conditions for the safe passage of vessels.
Another marine application is detecting oil spills, as outlined by Machteld Price from the European Maritime Safety Agency. Imagery from Sentinel-1 will be essential tools for supporting EU policies in maritime safety.
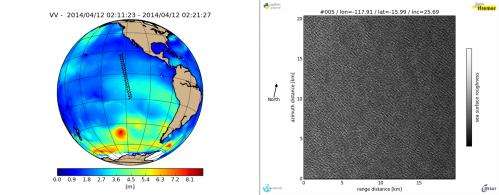
The spread of an oil spill can be forecast using information on waves, currents and winds – and such information can also be derived from the data. Bertrand Chapron from Ifremer in France can already see the benefits of the radar's high performance even before the satellite is fully calibrated.
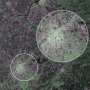
The mission also has many applications over land. Christiane Schmullius from the University of Jena used early images to demonstrate the mission's potential to map land cover over parts of Germany, differentiating between forests, agricultural areas and urban areas.
The 'radar interferometry' remote sensing technique was outlined by Alessandro Ferretti from the Tele-Rilevamento Europa in Italy. It combines two or more radar scans over the same area to detect ground movement down to a few millimetres between them.
As well as being a valuable resource for urban planners, this kind of information is essential for monitoring shifts from earthquakes, landslides and volcanic uplift.
Dr Ferretti also discussed how Sentinel-1 will foster development in European space and service industries, maximising opportunities for small and medium enterprises to grow.
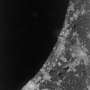
The Sentinel-1 mission is also already supporting humanitarian aid and crisis situations. Just 10 days after its launch, the satellite captured an image of flooding in the Caprivi plain from the Zambezi River in Namibia. The image was downloaded within two hours and the resulting products were available in less than an hour.
Jan Kucera from the Joint Research Centre outlined how this timely information offers a clear picture of the extent of inundation, and can be used to for assessing the damage to property and the environment.
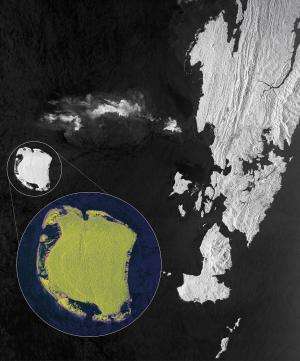
Sentinel-1 continues more than 20 years of radar imagery from satellites. This archive is not only essential for practical applications that need long time series of data, but also for understanding the long-term effects of climate change, such as those on Arctic sea-ice cover, continental ice sheets and glaciers.
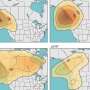
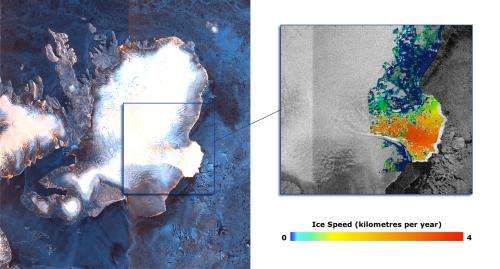
Andrew Shepherd from the UK's University of Leeds has already used some of the mission's early data to demonstrate the rapid movement of the Austfonna ice cap in Norway's Svalbard archipelago.
Combining new Sentinel-1 coverage with data from the German TerraSAR-X mission, he discovered an acceleration in ice motion in the southeastern section, which is now flowing at least 10 times faster than previously measured.
More early results from the new satellite were also presented at the Brussels event. Although the satellite is not yet in its operational orbit, nor is it calibrated for supplying true data, the images offer a taste of what's to come in the near future.
"It's truly amazing to get so much positive feedback from the user community at such an early stage in the mission," said Volker Liebig, Director of ESA's Earth Observation Programmes.
"We now look forward to the satellite's 'operational phase' to realise its full potential."
From 9 May, initial samples of Sentinel-1 prequalified products will be accessible through a new portal.
Provided by European Space Agency