Engineers explain physics of fluids some 100 years after original discovery
Sunghwan Jung is a fan of the 19th Century born John William Strutt, 3rd, also known as Lord Baron Rayleigh. An English physicist, Rayleigh, along with William Ramsay, discovered the gas argon, an achievement for which he earned the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1904.
But it was Rayleigh's lesser-known discovery of a physical phenomenon in 1878 that was more intriguing to Jung. Some 135 years ago, Rayleigh wrote that two fluid jets or drops do not always merge into one body of liquid, a counter-intuitive topic or phenomena in physics that has since been studied in much detail, cited Jung, Virginia Tech assistant professor of engineering science and mechanics.
The significance today of this fact is that when noncoalescence takes place between two fluids, it might impact a variety of industrial and everyday processes such as fuel efficiency, ink jet printing, and the development of spray coatings.
New information on Rayleigh's verbal description of the collision of fluids now appears in a contemporary paper authored by Jung and Pavlos Vlachos, professor of mechanical engineering at Virginia Tech, and Navish Wadhwa, of Blacksburg, Va., a doctoral candidate in engineering science and mechanics. The paper, accepted in Physical Review Letters, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Physical Society, is called "Noncoalescence in the oblique collision of fluid jets."
"In Rayleigh's original paper, he mentioned two things: drop bouncing on a liquid bath and jets bouncing. No pictures were given. Much work has been done in drop-bath bouncing, but no work has been done in bouncing jets except for a couple of demonstrations in textbooks. We are the first ones to rationalize the physical mechanism of bouncing jets," Jung explained.
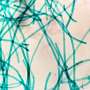
In their experiments, the researchers studied two silicone oil jets bouncing off each other upon collision. Silicone oil is used in most experiments in order to avoid any surface contamination, Jung said, and it is often the base for hydraulic fluids or lubricants.
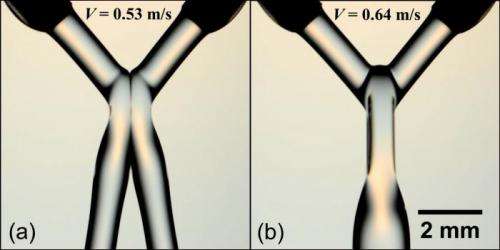
"Intuition tells us that two or more jets of the same fluid impinging into each other will readily coalesce to form a single mass of fluid, and are well-studied phenomena," Jung explained.
Velocity is key to bringing the two silicone oil jets into a single flow of liquid. Since these jets of fluid drag along air, considered to act as a cushion, the two jets will bounce off of each other. But when the speed of the flow is increased beyond a certain threshold, the air is no longer stable due to the high inertia of jets, and the liquid jets will coalescence, Jung added.
To attain fuel efficiency in space rockets, two different fuel fluids need to mix well to maximize the combustion.
"In our experiments, we showed they are able to bounce off each other and inhibit the mixing. However, in rocket fuel tanks, the fluids come out of the nozzles are a very high speed, so no bouncing happens in their cases," Jung said.
Jung's earlier work on fluid flow won him the 2010 international Milton Van Dyke award at the 63rd annual meeting of the American Physical Society.
Journal information: Physical Review Letters
Provided by Virginia Tech