Last update:
Condensed Matter news

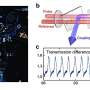
Researchers advance new class of quantum critical metal that could advance electronic devices
A new study led by Rice University's Qimiao Si has unveiled a new class of quantum critical metal, shedding light on the intricate interactions of electrons within quantum materials. Published in Physical Review Letters on ...
Condensed Matter
17 hours ago
0
123

Unlocking the secrets of diamond: New insights into nitrogen-vacancy center formation
Research teams from Wuhan University and the China University of Geosciences (Wuhan) have revealed new insights into the formation mechanism of nitrogen-vacancies (NV) centers in type-Ib diamonds, a phenomenon critical to ...
Condensed Matter
18 hours ago
0
1

Physicists capture images of atoms flowing along a boundary without resistance despite obstacles in their path
Typically, electrons are free agents that can move through most metals in any direction. When they encounter an obstacle, the charged particles experience friction and scatter randomly like colliding billiard balls.
Condensed Matter
19 hours ago
0
93

Nuclear fuel experiment demonstrates how liquid plutonium oxide behaves at the hottest temperatures
The 2011 accident at the Fukushima-Daiichi plant in Japan inspired extensive research and analysis that elevated nuclear energy into a standard bearer for safety. It also inspired a number of studies at the U.S. Department ...
Condensed Matter
Sep 5, 2024
0
89

Adding an alternating magnetic field to layers of twisted graphene creates even more exotic properties
Magnetic fields can engineer flat bands in twisted graphene layers to create a new playground for exotic physics, RIKEN physicists have shown.
Condensed Matter
Sep 5, 2024
0
1

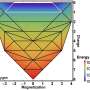
Physicists capture first thickness-dependent transitions in two-dimensional magnetic material
A team of physicists from The University of Hong Kong (HKU), Texas Tech University (TTH), and the University of Michigan (UMich), has made an important discovery in the study of van der Waals (vdW) magnetic materials, a special ...
Condensed Matter
Sep 5, 2024
0
46

Optoelectronic diamond device reveals an unexpected phenomenon reminiscent of lightning in slow motion
Diamond is in many ways the ultimate material. Besides its enduring aesthetic value, diamond is also a highly versatile industrial material. While its claim as the hardest substance known to science has been usurped by ultra-rare ...
Condensed Matter
Sep 4, 2024
0
54

Researchers demonstrate spontaneous synchronization of quantum vortices in semiconductor microcavities
Researchers from Skoltech, Universitat Politècnica de València, Institute of Spectroscopy of RAS, University of Warsaw, and University of Iceland have demonstrated the spontaneous formation and synchronization of multiple ...
Condensed Matter
Sep 3, 2024
0
44

Creating an 'imprint' on a super photon
Thousands of light particles can merge into a type of "super photon" under certain conditions. Researchers at the University of Bonn have now been able to use "tiny nano molds" to influence the design of this so-called Bose-Einstein ...
Condensed Matter
Sep 2, 2024
0
204

Study predicts a new quantum anomalous crystal in fractionally filled moiré superlattices
Moiré superlattices, structures that arise when two layers of two-dimensional (2D) materials are overlaid with a small twist angle, have been the focus of numerous physics studies. This is because they have recently been ...

Non-Hermitian skin effect in all dimensions tied to point-gap topology
A study, published in the journal Science Bulletin and led by Dr. Haiping Hu from the Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOP, CAS), explores the non-Hermitian skin effect (NHSE) and non-Bloch bands.
Condensed Matter
Aug 30, 2024
0
18

Strong interlayer magnetic exchange coupling in La3Ni2O7-δ revealed by inelastic neutron scattering
Recently, an inelastic neutron scattering work on the bilayer nickelate La3Ni2O7-δ polycrystal finished by a team from Sun Yat-sen University was published in Science Bulletin. The team employed neutron spectroscopy to study ...
Condensed Matter
Aug 30, 2024
0
1

Researchers create entangled quantum magnets with protected quantum excitations
When different quantum states combine, new collective states of matter can emerge. In the quantum realm, combining components such as atoms that possess quantum effects can give rise to macroscopic quantum states of matter, ...
Condensed Matter
Aug 29, 2024
0
67

Physicists predict existence of new exciton type
Bruno Uchoa, a professor of condensed matter physics, and Hong-yi Xie, a postdoctoral fellow in condensed matter physics at the University of Oklahoma, have published research in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy ...
Condensed Matter
Aug 27, 2024
0
162

Kagome superlattice method offers new way to tune graphene's electronic properties
A research team has introduced a novel method for selectively tuning electronic bands in graphene. Their findings, published in Physical Review Letters, showcase the potential of artificial superlattice fields for manipulating ...
Condensed Matter
Aug 27, 2024
0
141

Sound drives 'quantum jumps' between electron orbits
Cornell University researchers have demonstrated that acoustic sound waves can be used to control the motion of an electron as it orbits a lattice defect in a diamond, a technique that can potentially improve the sensitivity ...
Condensed Matter
Aug 26, 2024
1
180

Validation of superconductor theory: Cooper pairs display wave-like distribution in Kagome metals
A superconductivity theory proposed by a Würzburg physics team has been validated in an international experiment that showed Cooper pairs display wave-like distribution in Kagome metals. The finding will enable new technological ...
Condensed Matter
Aug 23, 2024
1
250

Ultrathin quantum light sources: Scientists show excitonic interactions boost efficiency of entangled photon generation
Scientists from the National University of Singapore (NUS) have shown that excitonic resonances and transitions between excitons can significantly increase the efficiency of generating entangled photon pairs. This could lead ...
Condensed Matter
Aug 19, 2024
0
132

Scientists uncover exciton behavior in van der Waals magnets
A research group led by scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory has uncovered details about the formation and behavior of mobile, microscopic, particle-like objects called "excitons" ...
Condensed Matter
Aug 19, 2024
0
129

Physicists uncover new phenomena in fractional quantum Hall effects
Imagine a two-dimensional flatland, instead of our three-dimensional world, where the rules of physics are turned on their head and particles like electrons defy expectations to reveal new secrets. That's exactly what a team ...
Condensed Matter
Aug 15, 2024
0
166
More news

A new approach to fine-tuning quantum materials
New research challenges conventional wisdom on wet surface adhesion

Can quantum particles mimic gravitational waves?
'Kink state' control may provide pathway to quantum electronics
'Miracle' filter turns store-bought LEDs into spintronic devices
Physicists control electronic properties of moiré crystals
Other news

Nearby super-Earth has a sulfur-rich atmosphere, Webb observations suggest

Crystallized alternative DNA structure sheds light on insulin and diabetes

Scientists uncover mechanism preserving centromere during cell division

Solution to a cosmic mystery—the eccentric orbits of trans-Neptunian objects

Why are black holes stable against their own gravity?

Spontaneous supercrystal discovered in switching metal-insulator
A new way to control the magnetic properties of rare earth elements

Paving the way to extremely fast, compact computer memory
A new approach to accelerate the discovery of quantum materials

Researchers discover an effective and environment-friendly disinfectant

Antibody-like molecule shows promise for broad-spectrum malaria therapy

Researchers create a one-dimensional gas out of light

Mysterious 50-million-year-old fish to get a new genus

AI shines a new light on exoplanets