This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
How reef fish may use the moon's cycle to manipulate the sex of their offspring
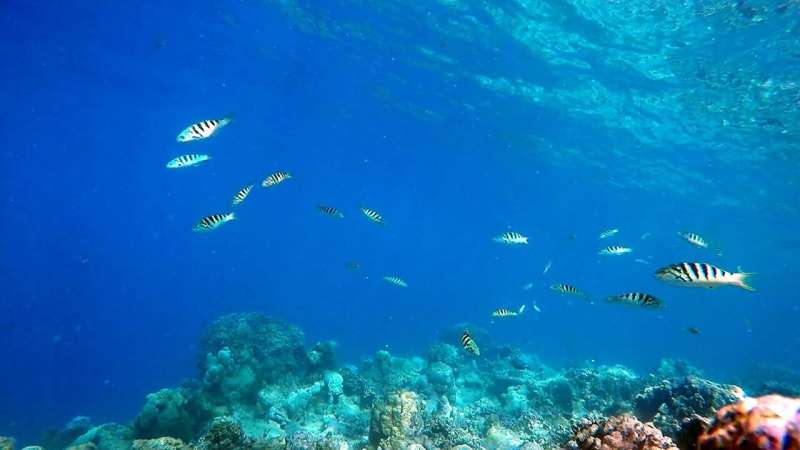

For some fish, being born close to a new moon increases the chances they will develop as male, while female offspring are more likely when the moon is full, a new study has found.
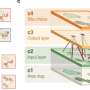
Lead author Jeff Shima, a professor of ecology at Te Herenga Waka—Victoria University of Wellington, said the study took a deep dive into the spawning patterns of the sixbar wrasse, a common resident of coral reefs in the Pacific. The study is published in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences.
"We've known sixbars spawn most often on the new moon, but this pattern has been particularly puzzling because offspring born at this time are least likely to survive. In contrast, offspring born closer to the full moon do much better.
"What we found is that in order to survive, sixbar offspring born on a new moon needed to alter their development rates, which ultimately shaped their sexual maturation and meant they were more likely to become male," said Professor Shima.
While sixbar parents spawning on a new moon are taking a high-stakes gamble on their progeny's survival, the study suggests it could be something of a calculated risk.
"Most of these babies won't survive, but the few that do are more likely to become male and that's akin to winning the lottery as males can produce many more offspring in the sixbar mating system.
"However, we think the spawning patterns of these fish may be calculated to spread their bets, with low-risk wagers (full moon spawning) coupled with some high-risk ones—in this case, spawning on the new moon."
Professor Shima says the findings raise the "intriguing possibility" that some species have evolved reproductive strategies that use the moon to help determine the sex of their offspring.
The moon's cycle has also been linked to the growth rates of young sixbars, which develop at sea for about seven weeks before making their home on coral reefs.
"As larvae, sixbar wrasse can lengthen or delay their development to arrive at the reefs at the most opportune times, under cover of darkness. Typically, this is on the night of the new moon."
Professor Shima says the study's finding will help inform research on other marine species.
"We know many marine organisms—fishes and invertebrates—reproduce on a lunar cycle. These patterns may be adaptive, allowing either the parents or their offspring to capitalize on the beneficial effects of tides or food availability, or to avoid predators.
"But we still have a lot to learn about when marine animals reproduce, and when, where, and how their offspring develop—in short, some of the greatest mysteries in nature."
However, as researchers work to unravel these mysteries, environmental changes caused by human activity are muddying the waters.
"Moonlight is affected by artificial light at night from coastal urban areas, as well as from dramatic changes in the distribution and intensity of cloud cover—a result of climate change. These human-induced changes in nocturnal illumination may have large, and largely unrecognized, consequences for the growth, survival, and reproductive success of organisms in some areas."
More information: Jeffrey S. Shima et al, Lunar rhythms and their carry-over effects may shape environmental sex determination in a coral reef fish, Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences (2024). DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2024.0613
Journal information: Proceedings of the Royal Society B
Provided by Victoria University of Wellington