This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Pyramid optical networks for unidirectional image magnification and demagnification

In Light: Science & Applications journal UCLA researchers introduce an innovative design for diffractive deep neural networks (D2NNs). This new architecture, termed Pyramid-D2NN (P-D2NN), achieves unidirectional image magnification and demagnification, significantly reducing the number of diffractive features required.
The results have broad applications in optical communications, surveillance, and photonic device isolation.
Diffractive deep neural networks (D2NNs) are optical systems composed of successive transmissive layers optimized through deep learning to perform computational tasks in an all-optical manner.
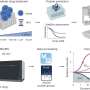
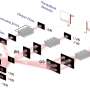
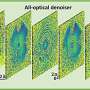
The UCLA research team, led by Professor Aydogan Ozcan, has developed a pyramid-structured diffractive optical network, which scales its layers pyramidally to align with the direction of image magnification or demagnification.
This design ensures high-fidelity image formation in one direction while inhibiting it in the opposite direction, achieving unidirectional imaging with fewer diffractive degrees of freedom. The researchers also demonstrate that by cascading multiple P-D2NN modules, higher magnification/demagnification factors can be achieved, showcasing the system's modularity and scalability.
The P-D2NN architecture was experimentally validated using terahertz (THz) illumination. The diffractive layers, fabricated through 3D printing, were tested under continuous-wave THz illumination.
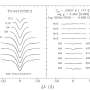
The experimental results, involving different designs for magnification and demagnification, closely matched the numerical simulations. The outputs in the forward direction accurately reflected the magnified or demagnified input images, while the outputs in the backward direction produced low-intensity, non-informative results, as desired for unidirectional imaging.
Applications and future prospects
The P-D2NN framework's ability to suppress backward energy transmission while dispersing the original signal into unperceivable noise at the output makes it a promising tool for various applications. These include optical isolation for photonic devices, decoupling of transmitters and receivers in telecommunications, privacy-protected optical communications, and surveillance.
Moreover, the system's polarization-insensitive operation and ability to deliver high-power structured beams onto target objects while protecting the source from counterattacks highlight its potential in various defense-related applications.
More information: Bijie Bai et al, Pyramid diffractive optical networks for unidirectional image magnification and demagnification, Light: Science & Applications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41377-024-01543-w
Journal information: Light: Science & Applications