This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
AI peers into the deep: High-resolution 3D tracking of coral reef fish

A study by the Leibniz Center for Tropical Marine Research (ZMT) is employing new methods in coral reef research. Under the leadership of fish ecologist Dr. Julian Lilkendey, an international research team utilized innovative AI technologies to analyze the movements of reef fish in the Red Sea with high precision.
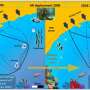
The study, recently published in the journal Ecology and Evolution, combines stereo-video technology with AI-driven 3D tracking. The method provided detailed insights into the movement patterns and energy expenditure of two surgeonfish species in their natural habitat in the Red Sea.
The researchers initially observed that the Brown surgeonfish (Acanthurus nigrofuscus) showed a preference for algae growing on dead corals during foraging, while the Yellowtail tang (Zebrasoma xanthurum) utilized a broader food spectrum and also grazed on algae found on sedimentary rock, coral rubble, and sand.
The notion of "peering into the deep" is evident on multiple levels. Spatially, the researchers captured the three-dimensional movement of fish during foraging on the coral reef using calibrated stereo-video systems, which goes far beyond conventional two-dimensional observations, according to lead author Lilkendey. The depth of insight was further enhanced through AI algorithms, which allowed for precise measurements of energy expenditure.
Targeted training of the AI model for species recognition
Initially, the pre-trained program YOLOv5 (You Only Look Once version 5) was employed, a neural network for real-time object detection. For the study, YOLOv5 was fine-tuned with additional background images from the Red Sea to better recognize fish in the video recordings. Subsequently, the neural network classified the detected fish by species.
A particular challenge was the targeted training of this AI model for species recognition. "Because there were few specific training images for the two surgeonfish species and the region, we relied on media from the citizen science website 'iNaturalist'", explains Lilkendey. "This allows us to use a variety of publicly accessible photos."
For the subsequent three-dimensional data acquisition, the scientists employed the so-called DeepSORT algorithm (Simple Online and Realtime Tracking with a Deep Association Metric). "This algorithm enables robust multi-object tracking by following the detected fish across consecutive video frames," Lilkendey says.
"DeepSORT can track the movements of individual fish even when they temporarily disappear from view or are obscured by other objects. By integrating the 3D information from the stereo image pairs, the algorithm generates precise three-dimensional movement patterns of the fish."
By coupling this with an approach to modeling their energy expenditure, the research team gained new insights into the ecology of the surgeonfish species.
"The Brown surgeonfish demonstrated specialized feeding behavior, preferring certain algae growing on specific substrates, in contrast to the generalized feeding behavior of the Yellowtail tang," reports Lilkendey. "Despite their low biomass, both species significantly contribute to reef grazing, using the energy obtained from food with similar efficiency in their movements."
Role of surgeonfish in maintaining the ecological balance in coral reefs
These findings underscore the importance of niche partitioning and the role of surgeonfishes in maintaining the ecological balance in coral reefs. "Changes in feeding behavior and energy budgets of surgeonfishes can influence algal growth and coral larval recruitment, thereby affecting the health and biodiversity of the entire reef ecosystem," Lilkendey continues.
Through this advanced analysis, the researchers have been able to peer more deeply into the functioning of marine ecosystems, laying the foundation for a better understanding of how energy is absorbed, transformed, and distributed within the reef.
Dr. Lilkendey stresses, "With high spatial and temporal resolution, we were able to analyze the three-dimensional movements of many fish in a coral reef simultaneously. Our innovative methodological approach allows us to peer deeper into the complexity of fish behavior and resulting energy flows."
The research methodology also opens up new possibilities for deriving "Energy Seascapes"—detailed representations of the energy expenditure of animals in marine ecosystems. Such mappings are crucial for developing effective health indicators and novel protection measures for reefs.
More information: Julian Lilkendey et al, Herbivorous fish feeding dynamics and energy expenditure on a coral reef: Insights from stereo‐video and AI‐driven 3D tracking, Ecology and Evolution (2024). DOI: 10.1002/ece3.11070
Journal information: Ecology and Evolution
Provided by Leibniz-Zentrum für Marine Tropenforschung (ZMT)