This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Science, social studies classes can help young English-learning students learn to read and write in English
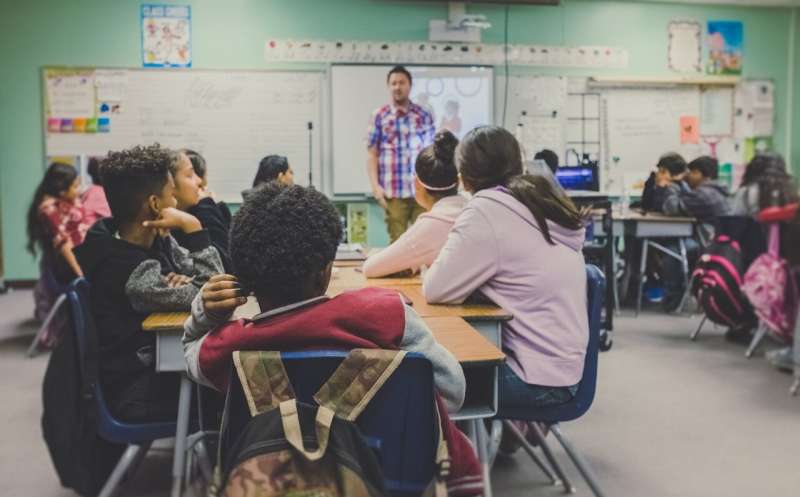

A new study finds that science and social studies classes may also help young students learn English, even when those classes include difficult and technical vocabulary. The paper is published in the Journal of Educational Psychology.
The study, which observed first- and second-grade students in 30 elementary schools in North Carolina, encouraged teachers to keep their English-learning students in class during science and social studies lessons. Science and social studies textbooks in those grades are often relatively technical and difficult for students, so traditional teaching methods in North Carolina encourage teachers to remove English-learning students from those content classes to focus on their language skills instead.
By creating a 10-week literacy program—known as a Tier 1 intervention—which kept English-learners in science and social studies classes, researchers found that those students saw improvements in their ability to write argumentative essays and use new academic vocabulary. The study highlights the importance of giving English-learners access to academic content, said Jackie Relyea, corresponding author of the study and assistant professor of literacy education at North Carolina State University.
"This study shows how important it is to provide equitable opportunities for English-learners to build knowledge in science and history, and to apply that knowledge through informational texts alongside their peers," Relyea said. "What we found was that when English-learners have access to content-rich literacy instruction, they develop content knowledge as well as language, reading comprehension, and writing skills."
The program used methods like interactive read-alouds, collaborative research and concept mapping to build students' vocabulary and understanding of complex topics. Concept mapping refers to using diagrams or similar visual aids to depict connections between ideas.
Significantly, the study found that English-learners had similar levels of improvement in science and social studies vocabulary and argumentative writing as their English-proficient classmates across the 10-week program. Notably, the intervention did not lead to negative results elsewhere, which supports the idea that English-learning students can attend more complex classes without falling behind. This further suggests that content-rich literacy instruction may help narrow the achievement gap between English-learners and their peers.
The intervention also modified classes to cover individual subjects for longer. That way, Relyea said, English-learners could get comfortable with a subject early on and then continue to get value from that knowledge later.
"One thing we noticed is the importance of using coherent text sets that focus on a single topic. In more traditional literacy instruction, our study found that topics tended to change quickly and there wasn't always a consistent throughline that the students could grab on to," she said.
"By focusing on similar subjects for longer, kids can dig deeper and develop more in-depth knowledge. It may be challenging at first, but when students encounter the same new words day after day, they become familiar with them and expand their vocabulary network. Staying on a thematic unit for longer periods also helps them become experts in the subject matter, which greatly enhances their vocabulary and comprehension skills."
The study challenges widely held assumptions about English-learners' academic capabilities, and highlights their readiness to engage with complex subject material despite their developing English proficiency. Relyea said that further research into incorporating small-group supplemental instruction could be valuable, potentially enhancing the effectiveness of the program even further.
More information: Jackie E. Relyea et al, Effects of tier 1 content literacy intervention on early-grade English learners' reading and writing: Exploring the mediating roles of domain-specific vocabulary and oral language proficiency., Journal of Educational Psychology (2024). DOI: 10.1037/edu0000882
Journal information: Journal of Educational Psychology
Provided by North Carolina State University