This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
3D covalent organic frameworks with zyg topology for photocatalytic synthesis of hydrogen peroxide
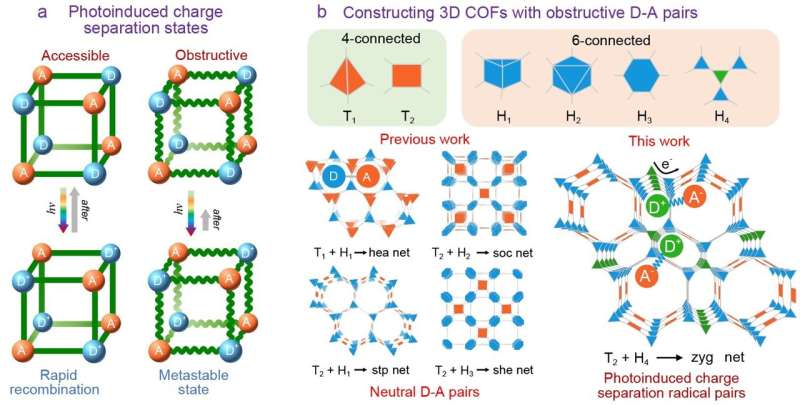
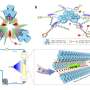
A research team proposed a new synthetic strategy of COFs based on a new topology that remotely separates donor (D) and acceptor (A) units in 3D lattice to produce the expected metastable photo-induced charge-separated states.
The researchers synthesized four 3D COFs with zyg topology for the first time by connecting unequal hexagonal monomers with a square building block. This structure type exhibits fused Olympic rings-shaped pores, forming two types of hexagonal channels with a maximum diameter of 3.5 nm, which provides a geometrical platform for stabilizing charge-separated states in the 3D lattice, as well as space for efficient guest transport.
Subsequently, the researchers obtained the photo-induced photochromic radical states in two zyg-type COFs containing photoactive electron donor moieties (triphenylamine and phenothiazine). The catalytic results combined with theoretical calculations revealed that the isolated radical states of these COFs performed better in the photosynthesis of H2O2 due to the enhancement of light-harvesting and carrier-transporting abilities as well as the reduction of activation energy of intermediates.
Remarkably, the radical state of the phenothiazine-based COF showed a H2O2 synthesis rate of 3324 μmol g-1 h-1, a significant increase in photocatalytic activity by 400% compared with the parent state, making it one of the best catalysts for the photocatalytic synthesis of H2O2.
This work will provide inspiration for the development of highly efficient 3D COF photocatalysts built on functional organic building blocks assembled in a topological structure that can facilitate light-induced charge separation.
The research is published in the journal National Science Review. The team includes Ya-Qian Lan and Yong Yan's group at South China Normal University (SCNU), with the first author of the paper being Ms. Tian-Tian Ma, a Ph.D. candidate at SCNU, and the corresponding authors being Profs. Ya-Qian Lan and Yong Yan at SCNU.
More information: Tian-Tian Ma et al, Photochromic radical states in 3D covalent organic frameworks with zyg topology for enhanced photocatalysis, National Science Review (2024). DOI: 10.1093/nsr/nwae177
Provided by Science China Press