This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Researchers find new ways to regulate hole transport layer for efficient perovskite solar cells
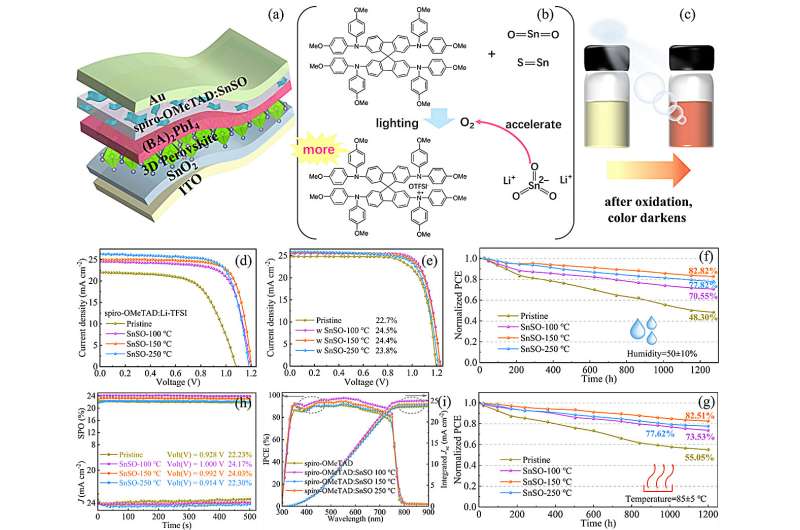
According to a study published in Nano Energy, a research group led by Prof. Chen Chong from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has increased the photoelectric conversion efficiency (PCE) of perovskite solar cells (PSCs) to 24.5%.
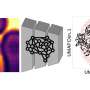
They used the inorganic nano-material tin sulfoxide (SnSO) as a dopant to oxidize and regulate the organic hole transport layer 2,2′,7,7′-tetrakis[N,N-di(4-methoxyphenyl)amino]-9,9-spirobifluorene (spiro-OMeTAD).
Spiro-OMeTAD is the most critical hole transport layer (HTL) material. To enhance the charge transport capability of spiro-OMeTAD, lithium trifluoromethanesulfonyl imide (Li-TFSI) is required to mediate the reaction between oxygen and spiro-OMeTAD.
However, this traditional doping method has low doping efficiency, and excessive Li-TFSI will remain in the spiro-OMeTAD film, leading to a decrease in the compactness and long-term conductivity of the film. The duration of the oxidation reaction usually takes 10 to 24 hours to reach the desired conductivity and work function.
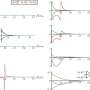
In this study, the researchers developed a fast and reproducible strategy to control the oxidation of the nanomaterial. They used SnSO nanomaterial to pre-oxidize spiro-OMeTAD to spiro-OMeTAD.+TFSI- free radicals in precursor solutions. This improved the conductivity, optimized the energy level position of HTL, and achieved a high PCE of 24.5%.
They found that the SnSO-regulated spiro-OMeTAD HTL has a pinhole-free, uniform, and smooth morphology. Both its performance and morphology remain stable even under high temperature and high humidity conditions.
"In addition, the oxidation process takes only a few hours, which is good for improving the commercial preparation efficiency of PSCs," said Prof. Chen Chong.
This study provides an effective strategy to further improve the efficiency and stability of PSCs, which is of great significance for promoting their commercialization.
More information: Mengqi Jin et al, A nanomaterial-regulated oxidation of hole transporting layer for highly stable and efficient perovskite solar cells, Nano Energy (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2024.109438
Journal information: Nano Energy
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences