This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Astronomers build a 3D map of dust within thousands of light-years
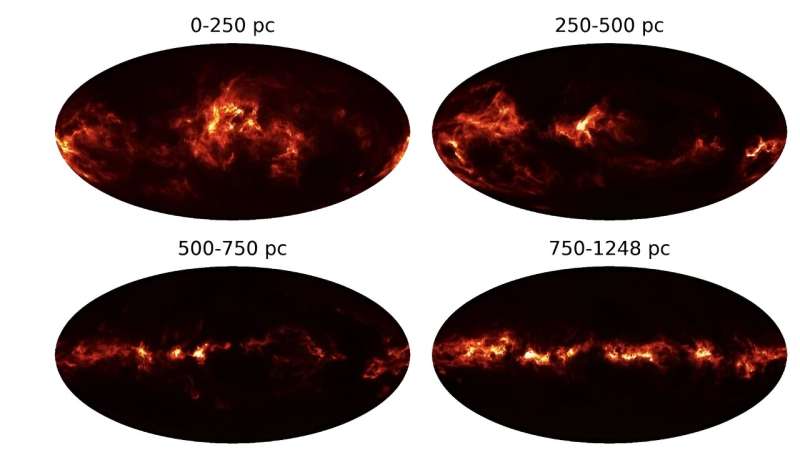
If you explore the night sky it won't be long before you realize there is a lot of dust and gas up there. The interstellar dust between the stars accounts for 1% of the mass of the interstellar medium but reflects 30% of the starlight in infrared wavelengths. The dust plays a key role in the formation of stars and the evolution of the galaxy. A team of astronomers has attempted to map the dust out to a distance of 3,000 light years and have just released the first 3D map of the dust in our galaxy.
The scattering and absorption of starlight by dust particles (extinction) allows us to explore dust clouds in three dimensions. It also tends to absorb shorter wavelengths from stars causing the stars obscured by the cloud to appear more red in color. By analyzing this it is possible to estimate the extent of dust extinction along our line of sight. When the distance measurements to the stars are taken into account it is possible to build a 3D map of dust clouds.
In understanding the distribution and collecting data for the model generation, Gaia has been a game changer. Gaia is the European Space Agency astrometry observatory that has been mapping the distances and positions of stars across the galaxy.
Since its launch 10 years ago, it has collected data from 1 billion stars, mostly within a few kiloparsecs of the sun (1 parsec is 3.26 light years). Knowing the position of stars accurately enables the reduction of errors in the dust extinction modeling. With the combination of stellar astrometry data, phototometric, extinction and spectroscopic data, now was the perfect time to investigate the three-dimensional distribution of dust in the Milky Way.
The study, by lead author Gordian Edenhofer from the Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics, was accepted for publication in Astronomy & Astrophysics. It is currently available on the arXiv preprint server. The team presents a three-dimensional dust map that goes further and deeper into space with greater resolution than ever before. The processing technique enabled the team to investigate dust distribution beyond 1 kiloparsec while also resolving nearby dust clouds with parsec-scale precision.
They were able to present the map of dust out to a distance of 1.25 kiloparsec in greater resolution than before. This was thanks to their use of distance and extinction estimates from previous studies that had lower uncertainties than other data sets. Their map has an angular resolution of up to 14 arc minutes and parsec-scale distance resolution. It's always pleasing to find a result that is in agreement with previous studies and existing 3D dust maps. But even more pleasing is when it goes further by improving the area of space covered and with a higher spatial resolution than before.
As is often the case—and one of the reasons I love science—the map is publicly available online and can be queried and viewed via a Python package by anyone interested. The team hopes that the maps will be used for further studies into the distribution of dust and the nature of the interstellar medium.
More information: Gordian Edenhofer et al, A parsec-scale Galactic 3D dust map out to 1.25 kpc from the Sun, Astronomy & Astrophysics (2024). DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202347628. On arXiv: DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2308.01295
Provided by Universe Today