This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Climate change has brought forward the flowering period in Doñana National Park by 22 days, finds study
Researchers from the University of Seville have investigated how the flowering of 51 species of shrubs, bushes and trees has changed over the last 35 years in Doñana National Park so as to understand how plant communities are responding to climate change in the south of the Iberian Peninsula.
Over this period, the average temperature in the area has increased by 1°C and the minimum temperature by as much as 2°C. As a result, the community's peak flowering time, the time when the greatest number of species are in flower, has been brought forward by 22 days, from 9 May to 17 April. The study is published in the Annals of Botany.
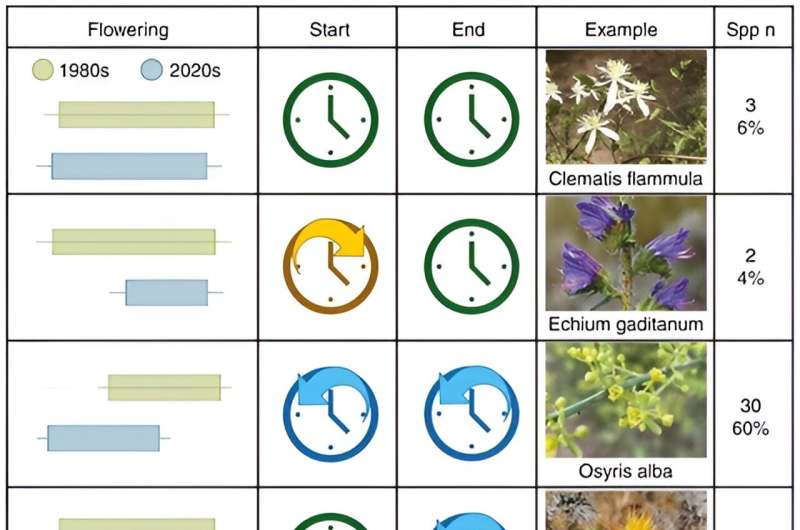
This earlier flowering is not due to only a few species; rather, 80% of the species have brought forward the onset of flowering, while 68% have brought forward the end of flowering. The most advanced species is rosemary (Salvia rosmarinus), which has been brought forward by 92 days.
Moreover, because flowering start and end dates are not being brought forward equally, many species are flowering for longer, leading to combinations of species in flower that did not previously flower together: 55% of species now find an "overcrowded" neighborhood of flowers, which can lead to increased competition for pollinating insects' attention.
Flowering is a key moment in the life of plants, since they reproduce sexually through flowers. For a plant to reproduce, it must flower at the same time as its neighbors, and since plants cannot move, they rely upon insects to carry pollen (containing the male gametes) from one flower to another, so the activity of plants and insects must be synchronized.
However, due to climate change, plants are flowering earlier in the northern hemisphere, as several studies published in Europe, Asia and North America have shown. Added to this problem is the fact that, in the Mediterranean, the impact of climate change is being felt more than in other parts of the world, with temperatures rising 20% faster than the global average.
Plants' response to climate change in the Doñana environment is among the largest described to date in the world. We know that plants need to "accumulate" hours of warmth to know when to flower, and they are possibly reaching the required amount much earlier. Some species may consequently produce fruit or germinate at less favorable times of the year (exacerbated by drought) or face unexpected competition from pollinators.
This research was possible due to the fact that the flowering of this plant community was studied in the 1980s. The aim of that study was a different one and it could not have been foreseen just how useful this data would prove to be in revealing the effects of climate change on our biodiversity.
Studies monitoring natural communities require long-term perspectives, which are often incompatible with the reality of research projects that have to be completed in the short term. In this case, basic research has enhanced our understanding of the magnitude of the effects of a global problem such as climate change on biodiversity and our environment.
More information: Daniel Pareja-Bonilla et al, Better soon than never: climate change induces strong phenological reassembly in the flowering of a Mediterranean shrub community, Annals of Botany (2023). DOI: 10.1093/aob/mcad193
Provided by University of Seville