This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Research proposes three-phase catalytic process for assembling nanoparticles to enhance SERS sensing
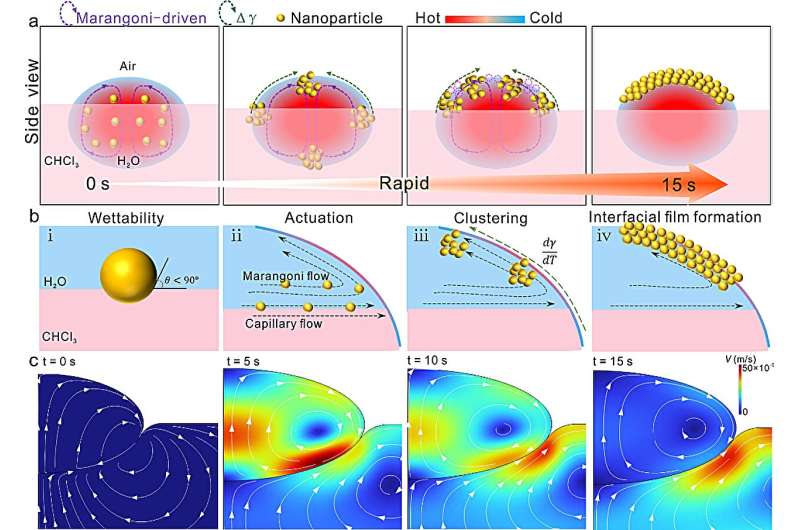
Recently, a research team led by Prof. Yang Liangbao from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed an innovative strategy for assembling small nanoparticles in a three-phase catalytic process, enabling enhanced surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) sensing.
The results were published in Analytical Chemistry.
Currently, there are difficulties in quickly and simply assembling high-density and large-area plasma multilayer films.
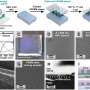
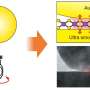
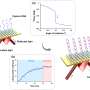
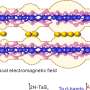
To address this issue, researchers introduced the concept of "catassembly" to enhance the rate and control of nanoparticle assembly dynamics. By dropping heated Au sols onto oil chloroform (CHCl3), this approach triggered a rapid assembly of plasmonic multilayers within 15 s at the oil-water-air (O/W/A) interface.
"Interfacial catassembly offered significant advantages by providing large-area, high-density plasmonic hot spots," said Xie Tao, a member of the team, "thus enabling highly sensitive and stable SERS sensing."
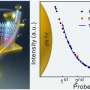
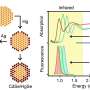
The plasmonic multilayers consisting of 10 nm gold nanoparticles exhibited remarkable sensitivity, detecting crystal violet molecules at concentrations as low as 1 nM. Moreover, these multilayers demonstrated excellent stability, with a relative standard deviation (RSD) of approximately 10.0%.
Importantly, these results were comparable to those achieved using traditional layer-by-layer assembly with 50 nm gold nanoparticles, challenging the conventional understanding of plasmon properties in small particles.
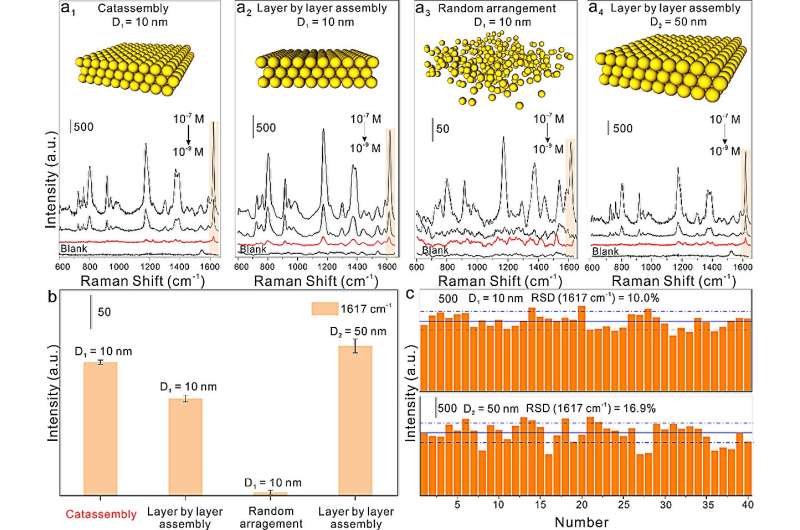
The three-phase catassembly method showcased the exceptional SERS sensitivity and stability of the plasmonic multilayers formed by 10 nm gold nanoparticles, paving the way for the application of small-nanoparticle SERS sensing.
More information: Tao Xie et al, Three-Phase Catassembly of 10 nm Au Nanoparticles for Sensitive and Stable Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Detection, Analytical Chemistry (2023). DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c02703
Journal information: Analytical Chemistry
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences